Short Range Laser Rangefinders (Short Range LRFs) are widely used in industrial automation, robotics, level measurement, and OEM systems where high accuracy, fast response, and compact size are more important than long-distance capability.
However, not all short range LRFs are the same.
This guide explains what defines a short range LRF, the key technical parameters to consider, and how to select the right model based on real application needs.
1. What Is a Short Range LRF?
A Short Range Telémetro láser typically refers to a laser sensor de distancia designed for measurement ranges from a few centimeters up to tens of meters, optimized for:
- High accuracy at close distances
- Fast measurement frequency
- Compact form factor
- Bajo consumo de energía
Short range LRFs are commonly based on phase-shift (iToF) measurement principles, which are well suited for precise distance detección in short to medium ranges.
2. Typical Applications of Short Range LRFs
Short Range Laser Range finders are widely deployed in scenarios such as:
- Industrial automation and positioning
- Conveyor belt object detection
- AGV / AMR obstacle detection
- Liquid level and material medición de altura
- Robotics and motion control
- OEM embedded measurement systems
In these applications, measurement stability and repeatability are often more critical than maximum range.
3. Key Parameters to Consider When Choosing a Short Range LRF
3.1 Measurement Range (Do Not Overspecify)
For short range applications, selecting an unnecessarily long range sensor often leads to:
- Higher cost
- Larger size
- Lower optimal accuracy at close distances
Best practice:
Choose a sensor whose maximum range is just above your real working distance.
Typical short range selections:
- Very close range: sub-meter to a few meters
- Standard short range: up to 10–25 m
- Extended short range: up to 40–60 m
3.2 Measurement Accuracy and Resolution
Short Range Laser Rangefinders are often chosen specifically for millimeter-level accuracy.
When evaluating accuracy, pay attention to:
- Absolute accuracy (e.g. millimeter-level)
- Distance-related error terms
- Repeatability and measurement stability
For precision positioning or level measurement, stable repeatability is often more important than headline accuracy numbers.
3.3 Measurement Frequency (Speed)
Measurement frequency determines how fast the sensor updates distance data.
Short range laser telémetro typically offer:
- Standard frequency for monitoring applications
- Higher frequency for fast-moving targets
High-frequency short range LRF are ideal for:
- Sistemas de transporte
- Dynamic object tracking
- Real-time control loops
For applications requiring fast response and real-time control, a high-frequency short range laser rangefinder is often the best choice.
High-frequency performance is easier to evaluate through real tests, and these high frequency laser distance sensor testing videos provide a clear reference.
3.4 Laser Type: Red vs Green
Short Range Laser Rangefinders commonly use visible lasers, each with different advantages:
Láser rojo
- Lower power consumption
- Rentable
- Suitable for indoor industrial environments
Láser verde
- Higher visibility to human eyes
- Better performance under strong ambient light
- More reliable on reflective or challenging surfaces
Green Short Range Laser Rangefinders are often preferred for outdoor or visually assisted alignment scenarios.
Green Laser Vs Red Laser: 6 Key Differences For Choosing The Best Sensor
3.5 Communication Interface
A Short Range Laser Rangefinders should match your system architecture.
Common interfaces include:
- UART / TTL for embedded systems
- RS485 / RS232 for industrial environments
- Modbus RTU for PLC integration
For industrial automation, RS485 with Modbus is often the safest and most scalable choice.
3.6 Size, Weight, and Integration
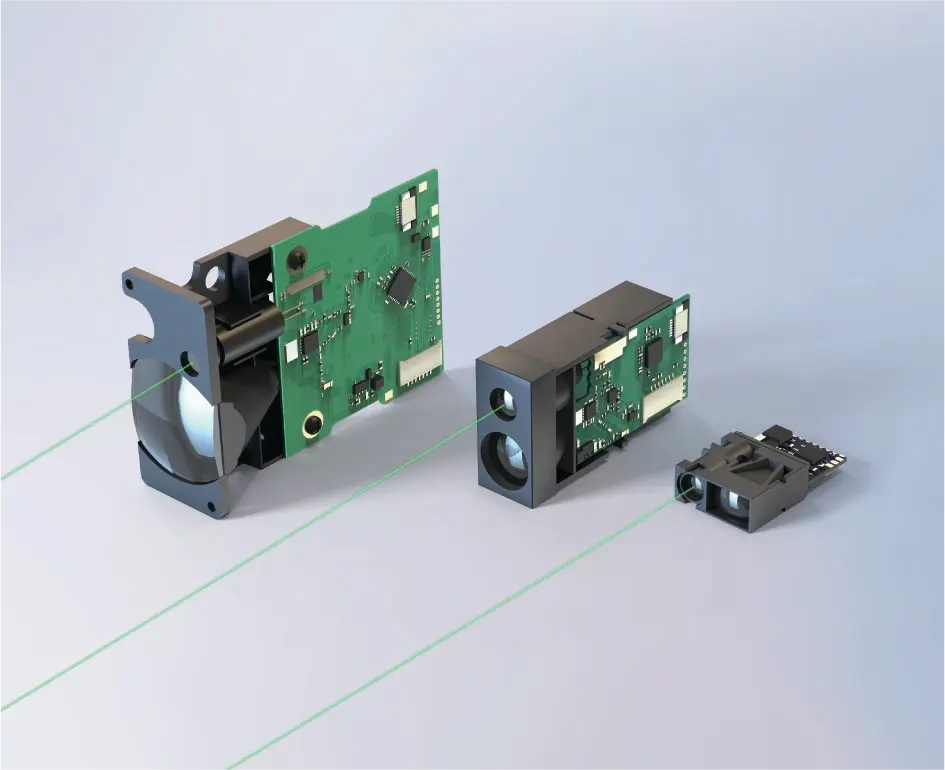
Short range sensors are frequently embedded into compact systems.
Important integration factors:
- Module dimensions
- Peso
- Connector or wiring method
- Mechanical mounting options
For OEM projects, compact modules significantly reduce integration complexity.
3.7 Environmental and Protection Requirements
Even short range sensors may operate in harsh environments.
Check:
- Temperatura de funcionamiento
- Protection level (e.g. IP-rated housings)
- Resistance to dust, moisture, and vibration
For factory or outdoor use, industrial protective housings can dramatically increase system reliability.
4. Short Range LRF Technology: Why Phase-Based Sensors Are Common
Most short range LRFs use phase-shift (indirect ToF) technology because it offers:
- High accuracy at close distances
- Tiempo de respuesta rápido
- Stable performance with low noise
- Compact optical and electronic design
This makes phase-based short range LRFs ideal for continuous measurement and control applications.
5. How to Match a Short Range LRF to Your Application
Choose a short range LRF if you need:
- High precision within short distances
- Fast measurement updates
- Compact and lightweight design
- Easy integration into industrial or OEM systems
Avoid overspecification if:
- Your working distance is fixed and limited
- You do not require long-range capability
- Power consumption and size are critical
Correct selection improves performance, reliability, and cost efficiency.
6. Typical Short Range LRF Selection Scenarios
| Aplicación | Key Selection Focus |
|---|
| Conveyor detection | High frequency, stable repeatability |
| AGV obstacle sensing | Fast response, industrial interface |
| Liquid level measurement | Accuracy, surface adaptability |
| Robotics positioning | Compact size, low latency |
| OEM embedded systems | Size, power, interface flexibility |
7. Conclusion: Selecting the Right Short Range LRF
A Short Range LRF is not simply a “shorter” laser rangefinder—it is a precision sensor optimized for close-distance performance.
When selecting a short range laser rangefinder, always evaluate:
- Real working distance
- Accuracy and stability
- Measurement speed
- Laser type
- Interface and integration needs
Choosing the right short range LRF ensures better system performance, easier integration, and long-term reliability.




PREGUNTAS FRECUENTES
-
What is a short range laser rangefinder?
A short range laser rangefinder (LRF) is a medición de la distancia device designed to measure targets at close distances, typically from a few centimeters up to several meters or tens of meters. It is commonly used in industrial automation, robotics, positioning systems, and precision measurement where fast response and high accuracy are required.
-
What is considered short range for a laser rangefinder?
In most industrial applications, a laser rangefinder is considered short range when its effective measurement distance is under 30 meters. Many high-precision short range LRFs operate within 0.1 to 10 meters, where accuracy, repeatability, and measurement speed are more important than maximum distance.
-
How do I choose the right short range laser rangefinder for my application?
To choose the right short range laser rangefinder, you should consider key factors such as measurement range, accuracy, sampling frequency, response time, target surface properties, and interface compatibility. For dynamic industrial systems, high-frequency and phase-based LRFs are often preferred for stable and real-time distance measurement.
-
What accuracy can a short range laser rangefinder achieve?
Short range laser rangefinders typically achieve accuracy from ±1 mm to sub-millimeter levels, depending on the measurement principle and operating conditions. Phase-based short range LRFs usually provide higher accuracy and better repeatability at close distances compared to pulse-based Sensores ToF.
-
Phase-based vs ToF: which is better for short range laser measurement?
For short range medición láser, phase-based sensors are generally better suited than pulse-based ToF sensors. Phase measurement offers higher accuracy, faster update rates, and more stable results at close distances, while ToF sensors are more commonly used for longer range or outdoor applications.
-
Why are high-frequency laser rangefinders important in short range applications?
High-frequency laser rangefinders are important in short range applications because they provide fast distance updates and low latency. This is critical for applications such as robotics, conveyor systems, and real-time control, where rapid movement or position changes require continuous and reliable measurement feedback.
-
Where are short range laser rangefinders commonly used?
Short range laser rangefinders are commonly used in industrial automation, robotics, AGVs, conveyor systems, material handling, and precision positioning applications. Their fast response and high accuracy make them suitable for environments where real-time distance monitoring is required.
-
What interfaces are commonly used with short range laser rangefinders?
Common interfaces for short range laser rangefinders include UART, RS485, analógico output, and industrial protocols such as Modbus. RS485 is often preferred in industrial environments due to its noise resistance and long communication distance.
https://meskernel.net/distance-sensor-module/