When comparing Modbus sensors vs analogique distance sensors in PLC systems, the key differences lie in accuracy, noise immunity, and scalability.
In PLC-based automation systems, mesure de la distance is commonly implemented using either analog distance sensors or Modbus sensors. Both technologies are widely used, but they differ significantly in accuracy, stability, wiring complexity, and diagnostic capabilities.
This article compares Modbus sensors and analog distance sensors from a practical industrial automation perspective, helping engineers and system integrators choose the right solution for PLC distance measurement.
Overview of Analog Distance Sensors
Analog distance sensors typically output a continuous electrical signal, such as 4–20 mA or 0–10 V, proportional to the measured distance.
Common Characteristics
- Simple signal processing
- Widely supported by PLC analog input modules
- Long history in industrial automation
However, analog signals are inherently sensitive to electrical noise, signal drift, and scaling errors, especially in harsh industrial environments.
Overview of Modbus Sensors
Modbus sensors transmit measurement data digitally using the Modbus RTU protocol, usually over an RS485 interface.
Key Characteristics
- Digital communication without signal drift
- High noise immunity via differential signaling
- Support for diagnostics and configuration
- Easy multi-sensor networking
Many industrial Modbus sensors—especially distance laser sensors—are designed for accurate, mesure sans contact in PLC systems.
For a broader explanation of industrial Modbus-based distance measurement technologies, refer to our Modbus laser distance sensor guide.
Signal Transmission: Digital vs Analog
One of the most important differences lies in how data is transmitted.
| Aspect | Analog Sensors | Modbus Sensors |
|---|
| Signal Type | 4–20 mA / 0–10 V | Digital (Modbus RTU) |
| Noise Sensitivity | Moyen à élevé | Very Low |
| Signal Drift | Possible | None |
| Cable Length Impact | Significant | Minimal |
Digital Modbus communication eliminates many uncertainties associated with analog signal transmission.
Accuracy and Measurement Stability
Analog sensors rely on precise voltage or current levels. Even small electrical disturbances can affect précision des mesures.
Modbus sensors transmit exact numerical values, often in millimeters, ensuring consistent accuracy regardless of cable length or electrical interference.
This makes Modbus sensors particularly suitable for applications requiring millimeter-level precision.
Wiring and Installation Complexity
Capteurs de distance analogiques
- Require dedicated analog input channels
- Scaling and calibration needed in PLC
- Susceptible to grounding issues
Modbus Sensors
- Use shared RS485 communication bus
- Minimal PLC-side scaling
- Simplified expansion for multiple sensors
From a system architecture perspective, Modbus sensors reduce wiring complexity in multi-point measurement systems.
Diagnostics and Maintenance
Analog sensors provide limited diagnostic information. Troubleshooting often requires manual signal measurement.
Modbus sensors can offer:
- Communication status
- Sensor error codes
- Configuration parameters
- Diagnostic registers
These features significantly reduce commissioning time and long-term maintenance effort.
Scalability in PLC Systems
Scaling is another key consideration:
- Analog systems require additional analog input modules as sensor count increases
- Modbus sensors allow multiple devices on a single RS485 bus
For systems with many distance measurement points, Modbus sensors provide a more scalable and cost-effective solution.
Typical Use Cases Comparison
| Application | Preferred Technology |
|---|
| Simple short-range measurement | Analog sensors |
| High-accuracy positioning | Modbus sensors |
| Long cable runs | Modbus sensors |
| Multi-sensor networks | Modbus sensors |
| Harsh industrial environments | Modbus sensors |


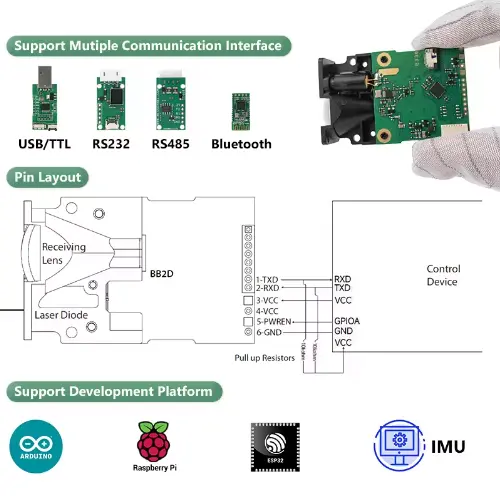

When Should You Replace Analog Sensors with Modbus Sensors?
Replacing analog sensors with Modbus sensors is recommended when:
- Measurement accuracy is critical
- Electrical noise causes unstable readings
- System scalability is required
- Diagnostics and remote configuration are needed
In many modern PLC systems, Modbus sensors are increasingly preferred for new designs.
Conclusion
Both analog distance sensors and Modbus sensors have their place in PLC systems. However, for applications demanding high accuracy, strong noise immunity, scalability, and diagnostics, Modbus sensors provide clear advantages.
For engineers designing new automation systems—or upgrading existing ones—Modbus sensors represent a robust and future-proof solution for PLC distance measurement.
For a complete overview of industrial-grade Modbus-based distance measurement solutions, see our Modbus Laser Distance Sensor for Industrial Automation guide.
Frequently Asked Questions – Modbus Sensors vs Analog Distance Sensors
-
What is the main difference between Modbus sensors and analog distance sensors?
The main difference between Modbus sensors and analog distance sensors is how measurement data is transmitted. Modbus sensors use digital communication (Modbus RTU over RS485), while analog distance sensors output continuous electrical signals such as 4–20 mA or 0–10 V.
-
Are Modbus sensors more accurate than analog distance sensors?
Yes, Modbus sensors are generally more accurate and stable than analog distance sensors. Digital Modbus communication eliminates signal drift and noise-related errors that commonly affect analog signals in industrial environments.
-
Which is better for PLC systems: Modbus sensors or analog distance sensors?
For modern PLC systems, Modbus sensors are usually the better choice when accuracy, noise immunity, scalability, and diagnostics are required. Analog distance sensors may still be suitable for simple or legacy PLC installations.
-
Do Modbus sensors work with all PLC brands?
Most Modbus sensors are compatible with PLCs that support Modbus RTU communication, including Siemens, Schneider, Omron, Mitsubishi, and Rockwell Automation PLCs with RS485 or Modbus modules.
-
Can Modbus sensors replace analog distance sensors in existing PLC systems?
Yes, Modbus sensors can replace analog distance sensors in many PLC systems, provided the PLC supports Modbus RTU communication. This replacement often improves measurement stability and reduces maintenance effort.
-
Are Modbus sensors less affected by electrical noise than analog sensors?
Yes, Modbus sensors are significantly less affected by electrical noise. RS485-based Modbus communication is designed for industrial environments and offers strong resistance to electromagnetic interference compared to analog signals.
-
Do Modbus sensors require less wiring than analog distance sensors?
In multi-sensor applications, Modbus sensors usually require less wiring. Multiple Modbus sensors can share a single RS485 communication bus, while analog sensors often need individual wiring and dedicated PLC analog input channels.
-
Which sensor type is better for long cable distances?
Modbus sensors are better suited for long cable distances. RS485 communication can reliably transmit data over hundreds of meters, while analog signals degrade more noticeably over long cable runs.
-
Are Modbus sensors easier to maintain than analog distance sensors?
Yes, Modbus sensors are easier to maintain because they provide diagnostic data, communication status, and error codes. Analog distance sensors offer limited diagnostics and often require manual troubleshooting.
-
When should analog distance sensors still be used instead of Modbus sensors?
Analog distance sensors may still be used in very simple PLC systems, low-cost applications, or legacy installations where Modbus communication is not available or cannot be easily added.
https://meskernel.net/laser-measure/