Single Point Laser Distance Sensors are becoming indispensable in modern industrial automation, robotics, and precision measurement. Unlike multi-point or 3D LiDAR systems, a single-point sensor focuses on one precise distance measurement at a time—achieving extremely stable, repeatable, and often millimeter-level accuracy.
In this guide, we break down how these sensors work, the differences between TOF and triangulation technologies, how accuracy is achieved, and where single point laser distance sensors are used across industries.
What Are Single Point Laser Distance Sensors?
Single Point Laser Distance Sensors are optical measurement devices that emit a laser beam and calculate the distance to a target based on the time or angle of the reflected light. They provide a single, highly accurate distance value, making them ideal for applications that require precision, speed, and reliability.
Typical performance features include:
Millimeter or sub-millimeter accuracy
Fast measurement frequency (10 Hz – 10 kHz depending on model)
Long working ranges from a few centimeters to several hundred meters
Robust performance on various materials (metal, concrete, reflective tape, etc.)
Compact size for easy OEM or industrial integration
How Single Point Laser Distance Sensors Work
Single point laser sensors generally rely on one of two optical principles:
1. Triangulation-Based Laser Sensors (Short Range, High Precision)
Triangulation sensors measure distance based on the displacement of a reflected laser spot onto a CMOS/CCD detector.
How it works:
- A laser beam hits the target surface.
- The reflected light forms a spot on the internal sensor.
- The spot position shifts depending on distance.
- Geometry + pixel shift → distance calculation.
Characteristics:
- Best for short range (0.05–2 meters)
- Achieves sub-millimeter accuracy
- Performs well with non-cooperative surfaces
- Sensitive to ambient light and angle
Applications:
- Thickness measurement
- Positioning in assembly lines
- Surface profiling
- Precision robotics
2. Time-of-Flight (TOF) Laser Sensors (Medium to Long Range)
TOF sensors calculate distance by measuring the time it takes for a laser pulse to travel to the target and back.
How it works:
- Sensor emits a laser pulse.
- Pulse reflects from the target.
- Sensor measures round-trip time (nanosecond scale).
- Distance = (Speed of Light × Time) / 2
Characteristics:
- Medium to long ranges (0.1–300+ meters)
- Millimeter-level accuracy with advanced filtering
- Excellent for moving targets
- Stable in outdoor conditions
Applications:
- UAV altitude measurement
- AGV/AMR navigation
- Outdoor surveying
- Industrial safety monitoring
- Level measurement (silos, tanks, cold storage)
Achieving Millimeter Accuracy in Distance Measurement
High-precision optical sensors combine multiple techniques to ensure stable measurement:
1. Temperature Compensation Algorithms
Sensors adjust internal calculations to offset component drift caused by heat or extreme cold.
This is essential for -20°C to -50°C cold-chain or high-temperature industrial environments.
2. Optical Filtering & Anti-Interference
- Narrow-band pass filters
- Adaptive averaging
- Ambient light suppression
These improve stability under sunlight, LED lighting, or reflective interference.
3. Multi-Point Sampling + Real-Time Processing
Fast sensors sample multiple points per measurement and calculate a stable, averaged output.
4. Precision Optics + Laser Modulation
High-quality optics and laser modulation schemes (AMCW for TOF, stable dot patterns for triangulation) improve consistency.
Advantages of Single Point Laser Distance Sensors
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|
| High accuracy | Millimeter-level measurement even at high speed |
| Compact design | Easy to integrate into robotic and industrial systems |
| Long range options | Up to hundreds of meters for TOF sensors |
| Non-contact measurement | No wear, suitable for harsh environments |
| Works on many surfaces | Metal, concrete, painted surfaces, reflective tape |
| Fast response time | Ideal for dynamic processes |
Key Industrial Applications
Single point laser distance sensors are used wherever precision distance measurement is required.
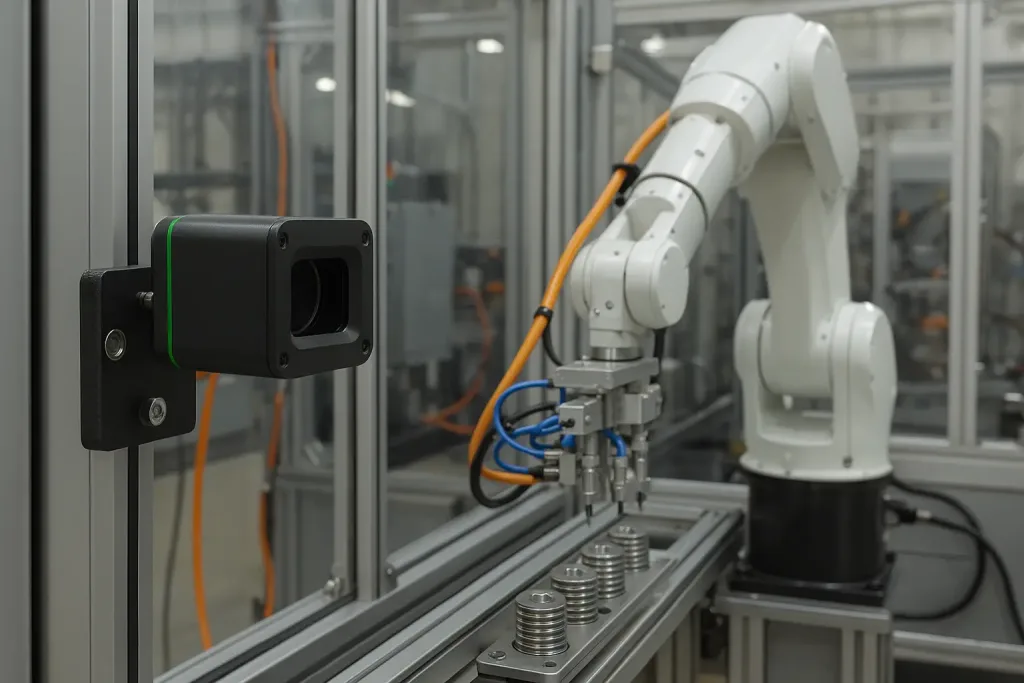





1. Industrial Automation & Positioning
- Robotic arm positioning
- Conveyor alignment
- Machine tool referencing
- Assembly line inspection
Why laser sensors?
High precision, fast measurement rate, non-contact reliability.
2. AGV / AMR Navigation
Laser distance sensors support:
- Docking accuracy
- Obstacle distance monitoring
- Lift height calibration
- Shelf positioning in warehouses
Compared to ultrasonic or infrared sensors, they offer:
- Better accuracy
- Longer range
- Higher repeatability
3. UAV & Drone Systems
Used for:
- Altitude hold
- Terrain following
- Precision landing
- Mapping / surveying assistance
TOF sensors perform well in:
- Outdoor sunlight
- High vibration
- Fast flight speeds
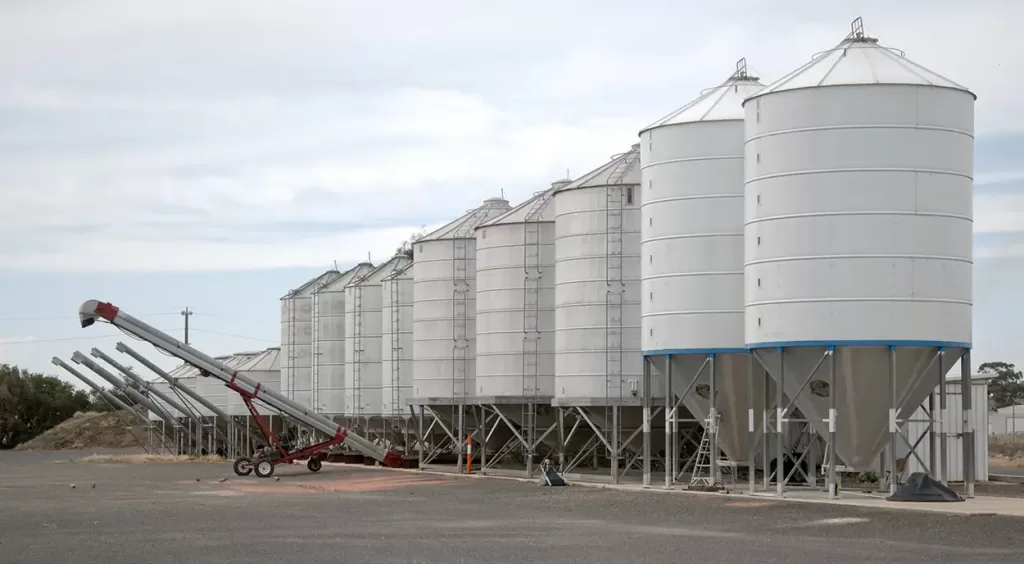
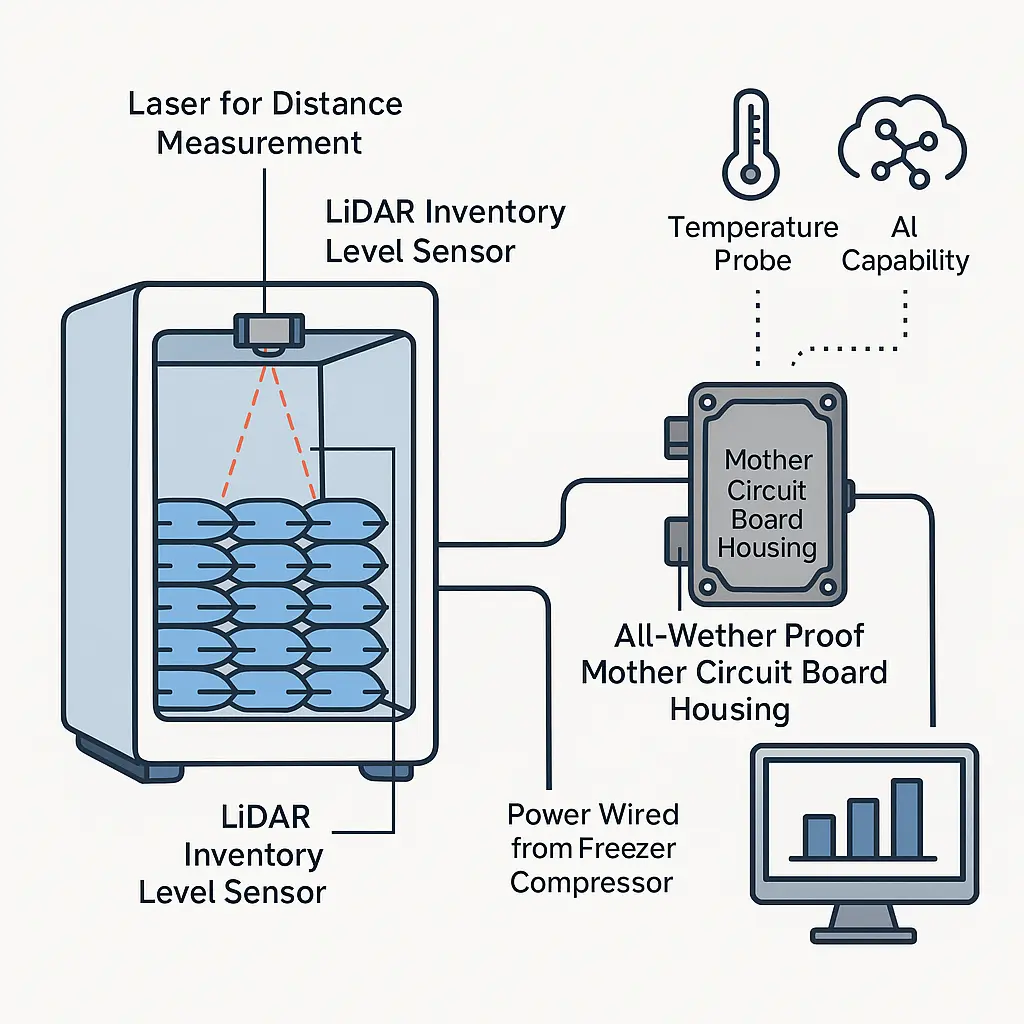
4. Level Measurement
Measure levels in:
- Silos
- Cold storage freezers
- Liquid tanks
- Grain warehouses
Laser sensors outperform ultrasonic sensors when:
- Temperature varies
- Dust or noise interferes
- Long distances are required
5. Manufacturing & Quality Control
- Thickness measurement
- Component alignment
- Displacement monitoring
- Deflection testing
Triangulation sensors provide the sub-millimeter accuracy required for precision manufacturing.
Single Point vs. Multi-Point Sensors: When to Choose Which
| Sensor Type | Best For | Typical Use |
|---|
| Single Point Laser Distance Sensor | Highest accuracy, cost-effective, fast response | Automation, AGVs, UAVs, industrial measurement |
| 2D/3D Scanning LiDAR | Mapping, obstacle detection, SLAM | Autonomous driving, mobile robots, surveying |
| Multi-Point Arrays | Surface profiling | Quality inspection |
If you need one precise distance, single-point sensors deliver better accuracy at lower cost.
Single Point Laser Distance Sensors are essential tools for accurate, reliable, and high-speed distance measurement in industries such as robotics, AGV navigation, UAV systems, and industrial automation. By understanding the differences between TOF and triangulation technologies—and how millimeter accuracy is achieved—engineers can select the optimal sensor for their application.
As industries continue to automate and digitize, single point laser distance sensors will remain a critical component for precision measurement and intelligent control systems.
-
What is a Single-Point Laser Distance Sensor?
A Single-Point Laser Distance Sensor is an optical device that measures the distance to a target using a single laser beam. It provides one precise distance reading at a time, often with millimeter-level accuracy, making it ideal for industrial automation, robotics, AGV navigation, and UAV height measurement.
-
How do single point laser distance sensors work?
These sensors work by emitting a laser beam and analyzing the reflected light.
They typically use one of two principles:
Time of Flight (TOF): measures the travel time of a laser pulse.
Triangulation: calculates distance from the angle shift of the reflected spot.
Both methods produce fast, non-contact, high-accuracy measurements.
-
What accuracy can Single Point Laser Distance Sensors achieve?
Most single-point laser sensors offer 1–5 mm accuracy, while high-end triangulation sensors can achieve sub-millimeter precision. Accuracy depends on optical design, temperature compensation, target reflectivity, and signal processing algorithms.
-
TOF vs Triangulation: Which is better?
TOF sensors are better for medium to long range (1–300+ m), outdoor use, and moving targets.
Triangulation sensors are better for short-range, high-precision applications requiring sub-millimeter accuracy.
The best choice depends on range, environment, and accuracy requirements.
-
What applications use single point laser distance sensors?
Common applications include:
Industrial automation and machine positioning
AGV/AMR navigation and docking
UAV altitude hold and precision landing
Level measurement in silos and cold storage
Quality inspection, thickness measurement, displacement testing
They are widely used in any environment requiring precise, stable distance readings.
-
Are single point laser distance sensors suitable for outdoor use?
Yes—TOF-based single-point sensors are highly suitable for outdoor environments.
They use optical filtering and ambient-light suppression to maintain stable performance in sunlight, fog, or dust. Triangulation models are more sensitive to bright light and are typically used indoors.
-
What materials can Single Point Laser Distance Sensors measure?
They work on:
Metal
Concrete
Painted surfaces
Plastics
Wood
Reflective tape or markers
Performance may vary depending on surface reflectivity and angle, but modern sensors include algorithms that compensate for weak returns.
-
How do these sensors achieve millimeter-level accuracy?
Millimeter accuracy comes from:
Temperature compensation
High-quality optics
Multi-sample averaging
Narrow-band optical filters
Precision calibration
Laser modulation techniques
High-end OEM sensors combine these methods to maintain accuracy across temperature changes and vibration.
-
What’s the difference between single point laser distance sensors and LiDAR?
A single-point laser sensor measures one distance value, while LiDAR scans multiple points to create a 2D or 3D map.
Choose single-point sensors when:
You need high accuracy
You measure a fixed direction or reference point
You need a cost-effective solution
LiDAR is better for mapping and navigation tasks requiring spatial awareness.
-
How to choose the right Single-Point Laser Distance Sensor?
Consider these factors:
Measurement range (short, mid, long)
Required accuracy
Surface type
Indoor vs outdoor environment
Update rate/frequency
Communication interface (TTL, UART, RS485, CAN, Analog 0–10 V)
Temperature range and environmental robustness
Matching the sensor to the application ensures maximum stability and performance.
-
Can single point laser distance sensors detect moving objects?
Yes. With measurement frequencies from 10 Hz to 10 kHz, TOF-based sensors can track fast-moving targets in real time, making them suitable for conveyors, robotics, and dynamic positioning systems.
-
Are single point laser distance sensors safe to use around humans?
Yes. Most industrial laser distance sensors use Class 1 laser diodes, which are safe for continuous human exposure and meet IEC/EN safety standards.
https://meskernel.net/distance-sensor-module/