Industrial-grade low temperature laser distance sensors designed for −20°C to −50°C. Featuring temperature compensation, optical filtering, and millimeter accuracy for UAVs, robotics, cold-chain systems, and outdoor surveying.
Accurate distance measurement becomes challenging in low-temperature environments. Laser transmitters, receivers, and timing circuits can all be affected by extreme cold, leading to unstable readings or large deviations.
Meskernel’s low-temperature laser distance sensors (such as LDL-S and LDL Low-Temperature Edition) are engineered to operate reliably from −20°C to −50°C, delivering stable millimeter-level accuracy for UAVs, outdoor robots, mining equipment, and cold-storage automation.
Why Low Temperature Affects Laser Distance Measurement
1. Laser Output Power Loss
Semiconductor lasers lose efficiency in cold environments. Lower output power reduces the return signal strength, especially in long-range applications.
2. Reduced Receiver Sensitivity (APD/PD)
Photodetectors become less responsive to weak reflections, increasing TOF noise and measurement jitter.
3. Timing Circuit Drift (MCU Time Base)
Cold temperature shifts the internal time base, causing direct distance errors of ±10–40 mm if not compensated.
Without proper temperature calibration, real-time compensation, and optical filtering, traditional laser sensors struggle in cold environments.
Temperature Compensation Technology
Meskernel sensors adopt multiple engineering techniques for extreme-weather measurement:
1. Full Temperature Calibration (−40°C to +60°C)
Each device is calibrated every 5°C to create a complete compensation curve for:
- time base
- laser output
- receiver gain
- systematic distance error
2. Real-Time Temperature Compensation
An onboard temperature sensor continuously monitors internal temperature. The MCU dynamically adjusts:
- laser driving current
- receiver amplification gain
- time-base parameters
This ensures stable measurement even at −20°C.
3. Optical Narrow-Band Filter
Snow-covered regions have extremely strong sunlight.
The optical filter blocks background noise and increases SNR by 30–60%.
4. Low-Temperature Laser Driver Circuit
The custom LDL driver maintains stable pulse energy under freezing conditions, ensuring long-range detection reliability.
Applications of Low Temperature Laser Distance Sensors



 Hunting Rangefinders
Hunting Rangefinders
1. UAV Altitude Hold & Obstacle Avoidance
Designed for Nordic regions, North America, plateau zones, and harsh winter flight conditions.
2. Outdoor Robotics & Mining Inspection
For snow-covered ground robots, winter patrol robots, and mining environments.
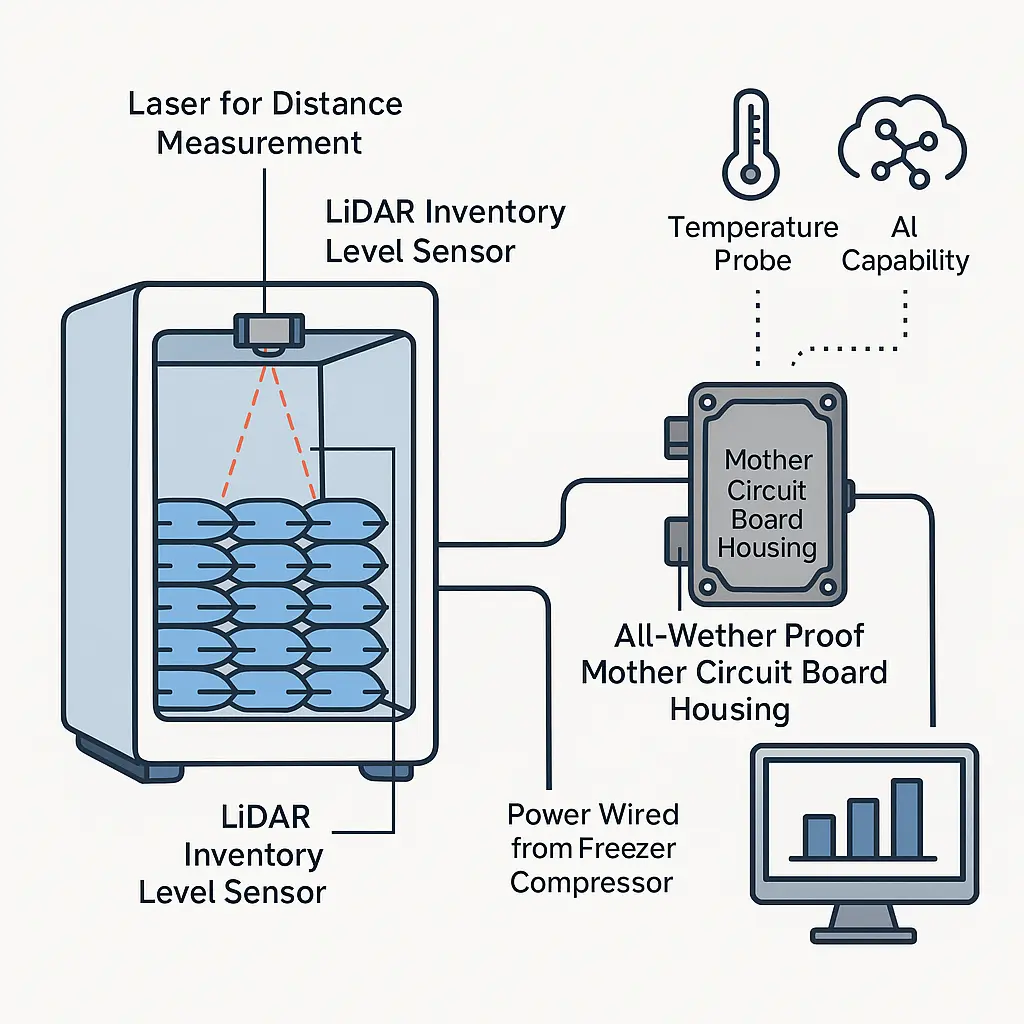
3. Cold-Storage and Frozen-Goods Monitoring
Used in freezers, cold rooms, and automated warehouse systems.
4. Surveying & Long-Range Mapping
Reliable measurement in forest, mountain, and wide-area outdoor environments.
Product Specifications
LDL Low-Temperature Edition
| Parameter | Value |
|---|
| Range | 0.2–30 m (outdoor) |
| Accuracy | ±3 mm |
| Operating Temperature | −20°C to +50°C |
| Update Rate | 3–20 Hz |
| Interface | UART / RS485 |
| Optical Filter | Yes |
| Temperature Compensation | Yes |
LDL-S UAV Distance Sensor
| Parameter | Value |
|---|
| Range | 0.2–50 m |
| Accuracy | ±1 mm |
| Operating Temperature | −20°C to +60°C |
| Update Rate | 3–20 Hz |
| Interface | UART (Pixhawk compatible) |
| Weight | <25 g |
| Application | UAV altitude hold |
Wiring Guide (LDL-S → Pixhawk UART)
- TX → RX
- RX → TX
- VCC → 5V
- GND → GND
Temperature Compensation Example – Performance Improvement
Cold environments easily cause measurement drift.
With temperature compensation, the error curve is significantly flattened—even at −20°C
FAQ: Low Temperature Laser Distance Sensors
-
Can laser sensors work reliably at −20°C?
Yes. With real-time temperature compensation and optical filtering, Meskernel sensors maintain ±2–3 mm accuracy.
-
Why does TOF drift in low temperature?
Cold temperature affects laser power, receiver sensitivity, and internal timing, causing distance error if not compensated.
-
Are these sensors suitable for drones?
Yes. LDL-S is designed for UAV altitude control, landing assistance, and outdoor obstacle detection.
-
What is a Low Temperature Laser Distance Sensor?
A Low Temperature Laser Distance Sensor is a specialized laser measurement device designed to operate reliably in freezing or sub-zero environments. These sensors contain temperature-compensated optical components and anti-condensation protection, ensuring stable distance readings in extreme cold conditions such as −20°C, −30°C, or even −40°C.
-
Why do standard laser distance sensors fail in cold environments?
Typical laser range sensors are not built for harsh conditions. In low temperatures, issues such as laser diode drift, internal condensation, lens freezing, and unstable ToF timing may occur.
In contrast, Low Temperature Laser Distance Sensors use enhanced optical filtering, sealed housings, and calibration algorithms to maintain accuracy.
-
What makes a Low Temperature Laser Distance Sensor suitable for outdoor winter applications?
Low Temperature Laser Distance Sensors are engineered with:
Temperature-compensated electronics
Heater-free low-power cold-start design
Optical filters to reduce sunlight interference
IP65/IP67 weatherproof enclosures
Frost-resistant lens coatings
These features allow the sensors to work in snow, frost, fog, and winter wind chill without losing performance.
-
What is the operating temperature range of most Low Temperature Laser Distance Sensors?
Most industrial-grade Low Temperature Laser Distance Sensors operate from −20°C to +60°C.
High-end modules, such as those used in drones or outdoor machinery, may support −30°C or −40°C depending on configuration.
-
How accurate are Low Temperature Laser Distance Sensors in sub-zero conditions?
A high-quality Low Temperature Laser Distance Sensor can maintain:
±1 mm precision at room temperature
±2–3 mm precision at −20°C or below
Stability is achieved through temperature drift compensation algorithms built into the sensor firmware.
-
Can Low Temperature Laser Distance Sensors be used on UAVs or drones?
Yes. They are widely used for:
Altitude hold in cold-weather UAV missions
Ice valley mapping
Snowfield terrain detection
Winter agricultural drones
Their compact size and stable low-temperature operation make them ideal for drone integration.
-
Do Low Temperature Laser Distance Sensors require heating modules?
Most modern Low Temperature Laser Distance Sensors do NOT require external heating, thanks to:
Built-in compensation chips
Low-drift laser diodes
Anti-fog optics
This makes installation easier and reduces power consumption—critical for drones and battery-powered devices.
-
What industries typically use Low Temperature Laser Distance Sensors?
Common industries include:
Drones & UAV autopilots
Cold chain logistics
Outdoor industrial automation
Wind turbine maintenance
Winter transportation systems
Mining in cold regions
Low-temperature laboratory equipment
These environments demand high-accuracy distance measurement under freezing conditions.
-
What measurement technologies do Low Temperature Laser Distance Sensors use?
Most rely on:
Time of Flight (ToF)
Phase-shift detection
Optical triangulation (in some short-range models)
ToF sensors are the most commonly used because they remain stable across large temperature changes.
-
How do Low Temperature Laser Distance Sensors handle snow or reflective surfaces?
They use:
Optical filters to block stray reflections
Adaptive gain control for bright snow backgrounds
Wavelength tuning to penetrate fog or light snowfall
Sensors designed for outdoor use typically incorporate intelligent signal processing for challenging surfaces.
-
Can Low Temperature Laser Distance Sensors measure through fog or ice?
They cannot “see through” thick ice or dense fog.
However, calibrated sensors with optical filtering and multi-pulse averaging can handle:
Light fog
Thin frost
Diffuse snowflakes
Performance depends on optical power and algorithm design.
-
What is the difference between a Low Temperature Laser Distance Sensor and a standard ToF sensor?
A Low Temperature Laser Distance Sensor includes:
Better temperature compensation
Improved low-noise signal paths
Cold-start stability
Stronger environmental sealing
Standard ToF sensors may lose accuracy when temperature fluctuates.
-
Are temperature-compensated laser sensors more expensive?
Yes, but the cost difference reflects:
Longer lifespan
Improved stability
Reduced maintenance
Higher outdoor reliability
For mission-critical systems such as drones or industrial robotics, the performance gain outweighs the small cost increase.
-
How can I choose the right Low Temperature Laser Distance Sensor for my project?
Choose based on:
Operating temperature range
Measurement distance
Required accuracy
Integration interface (UART, RS485, CAN, I²C, etc.)
Environmental protection (IP rating)
Optical filter requirements
Application type (UAV, surveying, industrial automation)
-
Does Meskernel provide Low Temperature Laser Distance Sensors?
Yes. Meskernel offers several Low Temperature Laser Distance Sensor modules specifically designed for:
Drone altitude systems
Outdoor automation
Cold storage monitoring
Snowfield measurement applications
Their sensors provide millimeter-level precision, temperature compensation, and long-range ToF measurement.
https://meskernel.net/laser-ranging/