LiDAR Sensor for Ocean Wave Monitoring | Marine Safety Solutions
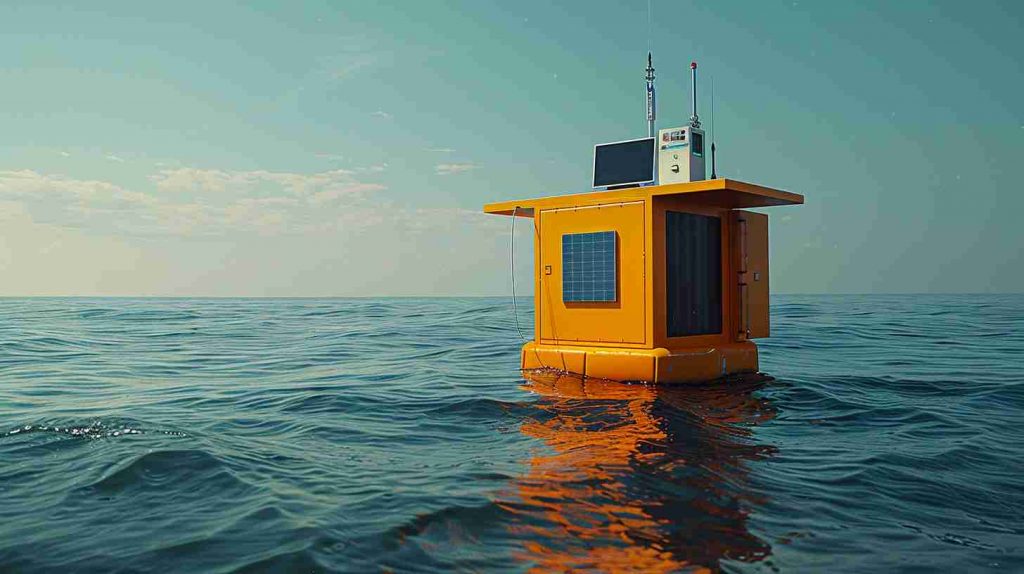

Why Ships Need a LiDAR Sensor for Wave Monitoring
For ship operators, oceanographers, and offshore engineers, wave conditions are more than a matter of comfort—they are a critical safety factor. Wave height, frequency, and direction impact navigation, energy efficiency, and marine research. Traditional methods, such as radar or buoys, often lack precision or require difficult deployment at sea.
This is where a Laser distance sensor for wave monitoring changes the game. By providing long-range, non-contact measurements, ships can detect and map ocean waves 100–200 meters ahead, enhancing both operational safety and data accuracy.
How a LiDAR Sensor Works on the Ocean
A LiDAR sensor (Light Detection and Ranging) emits laser pulses and calculates the time it takes for reflections to return from a surface—in this case, the moving ocean. This allows ships to capture real-time wave profiles, even at significant distances.
Key benefits of using a Laser distance sensor for ocean wave monitoring include:
- Long-range detection (100–200m): Anticipate waves before they reach the vessel.
- High accuracy: Millimeter-level precision enables reliable wave height and pattern analysis.
- Fast measurement frequency: With up to 20–50Hz sampling, a LiDAR sensor provides real-time wave data.
- Non-contact operation: Unlike buoys, LiDAR is maintenance-free and unaffected by rough seas.
Applications of a LiDAR Sensor in Marine Environments
LiDAR technology is increasingly adopted in marine industries because it provides accurate wave data without physical installations. Typical applications include:
- Ship Navigation & Safety
Ships use a distance sensor to predict wave impact and adjust speed or course.
- Oceanographic Research
Researchers can collect detailed wave datasets without deploying fragile floating equipment.
- Offshore Energy Platforms
Oil, gas, and renewable energy projects benefit from continuous wave monitoring.
- Autonomous Vessels
Unmanned surface vehicles (USVs) rely on a Laser distance sensor to detect waves for safe navigation.
How to Choose the Right LiDAR Sensor for Wave Measurement
When evaluating a Laser distance sensor for marine applications, key factors to consider are:
- Measurement Range: At least 100–200 meters.
- Frequency: High-frequency (20Hz+) for dynamic wave tracking.
- Accuracy: Millimeter resolution is best for scientific or safety-critical use.
- Durability: Waterproof (IP65+) and fog-resistant designs for harsh ocean environments.
- Interfaces: Compatibility with RS485, UART, or CAN ensures smooth integration with ship systems.
Why a LiDAR Sensor Outperforms Traditional Wave Monitoring Tools
Compared to marine radar or floating buoys, a distance sensor offers clear advantages:
- Easy deployment – no physical installation in the water.
- Lower maintenance – fewer failures in rough or icy conditions.
- Greater accuracy – laser-based LiDAR provides sharper resolution on water surfaces.
Future of Wave Mapping with a LiDAR Sensor
The future of marine navigation is digital and autonomous. A Laser distance sensor for ships will play an essential role by feeding data into AI-driven navigation systems. This integration will allow vessels to anticipate dangerous sea states and make smarter routing decisions.
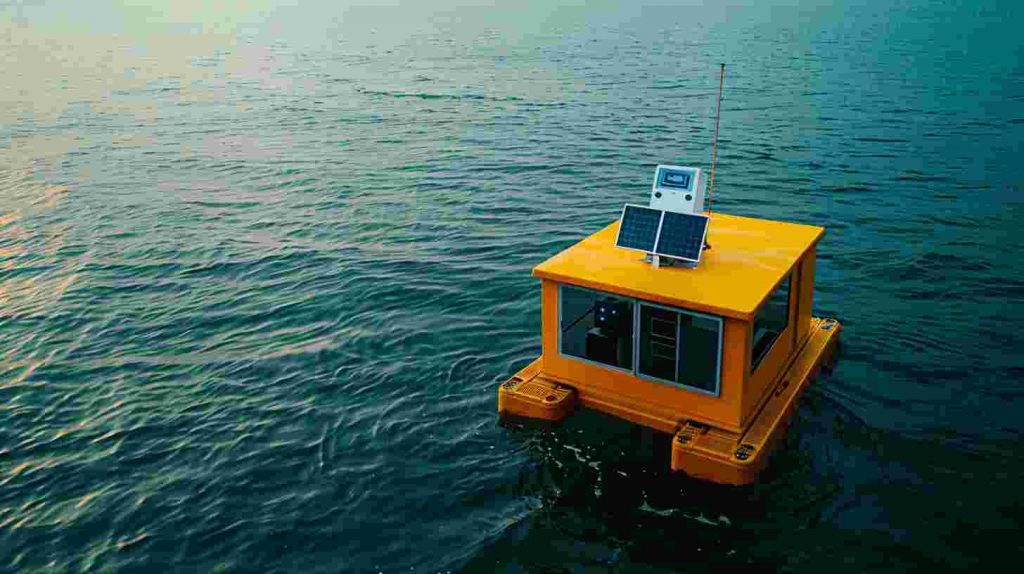





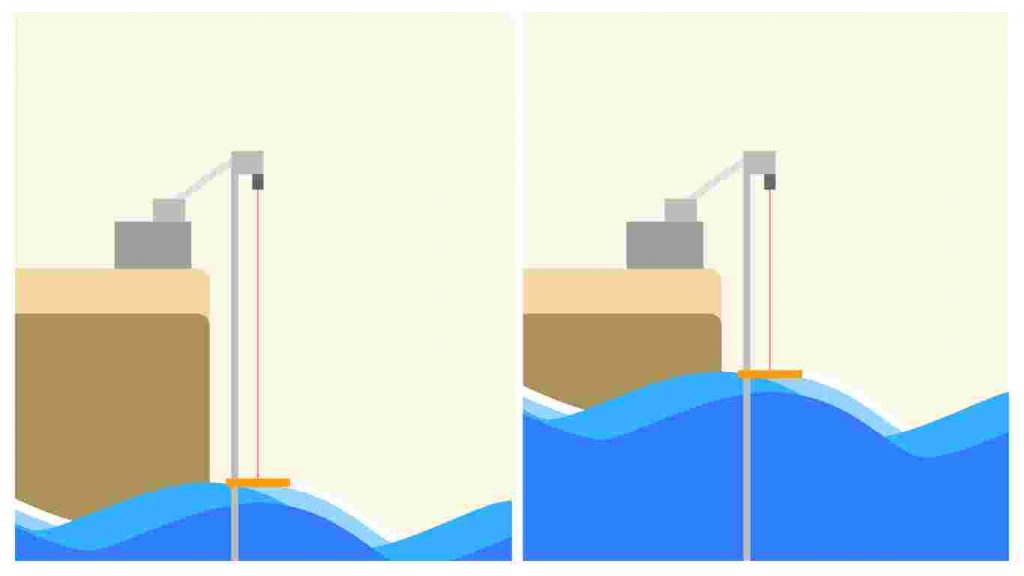
For anyone in shipping, research, or offshore engineering, a Laser distance sensor for ocean wave monitoring is an essential investment. It provides long-range, high-accuracy, real-time data that traditional methods cannot match.
If you’re looking for a customized Laser distance sensor solution for marine wave mapping, our engineering team at meskernel can help tailor a sensor to your ship’s requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Can a Laser sensor work reliably over the ocean surface?
Yes. A LiDAR sensor is designed to measure reflective surfaces like water. With millimeter-level accuracy and high-frequency sampling, it can capture ocean wave profiles in real time, even under challenging sea conditions.
Q2: What is the maximum range of a distance sensor for marine wave detection?
Depending on the model, LiDAR sensors can measure distances from a few centimeters up to 200 meters or more. For ship-based wave mapping, sensors with a 100–200m range are commonly used.
Q3: How does a Laser distance sensor improve ship navigation safety?
By detecting waves ahead of the vessel, a LiDAR sensor allows the crew or onboard systems to anticipate dangerous conditions, adjust speed or course, and prevent accidents caused by sudden wave impacts.
Q4: Besides ships, where else can LiDAR distance sensors be used for safety applications?
LiDAR sensors are widely used in:
Offshore energy platforms for sea-state monitoring.
Port and harbor safety systems to track tides and wave surges.
Autonomous marine vessels (USVs and unmanned ships).
Industrial safety zones for distance monitoring of moving equipment.
Mining and construction sites for collision avoidance.
Q5: How durable is a Laser-based sensor for marine environments?
Marine-grade LiDAR sensors are built with IP65 or higher protection levels, making them waterproof, dustproof, and resistant to fog and corrosion. This ensures continuous operation in harsh offshore conditions.
Q6: What data output formats do lidar tof sensors support for integration?
Most LiDAR sensors provide interfaces such as RS485, UART, or CAN, making them easy to integrate with ship navigation systems, data loggers, or AI-based safety software.
Q7: Can LiDAR tof sensors be customized for specific marine projects?
Yes. Manufacturers like meskernel can customize LiDAR sensors for range, frequency, housing, and communication interfaces to meet unique requirements in shipping, offshore energy, or research applications.
Q8: What industries outside of marine use distance measuring sensors for safety?
Transportation: Train and highway monitoring.
Aviation: Runway obstacle detection.
Warehousing & Logistics: Collision avoidance for AGVs and forklifts.
Smart Cities: Traffic flow and pedestrian safety monitoring.
https://meskernel.net/lidar-distance-sensor/