ToF sensor vs LiDAR explained: working principles, pros/cons, range, accuracy, and use cases. Discover the best laser distance sensor for drones, AGVs, robotics, and OEM integration.
Are ToF and LiDAR the Same?
Time-of-Flight (ToF) sensors and LiDAR are often mentioned together because both rely on light-based distance measurement. However, they serve very different purposes.
A ToF distance sensor is typically a compact, single-point or small-array module designed for short to medium range (from centimeters to several meters).
LiDAR, on the other hand, is usually a scanning laser system that creates 2D/3D maps for robotics, surveying, and autonomous navigation.
Choosing between them depends on your required range, precision, scanning coverage, speed, and environmental conditions—especially outdoors.
This guide provides a deep, technical, side-by-side comparison to help engineers, integrators, and OEM manufacturers choose the right solution.
Working Principle Comparison
Continuous Wave vs. Time-of-Flight
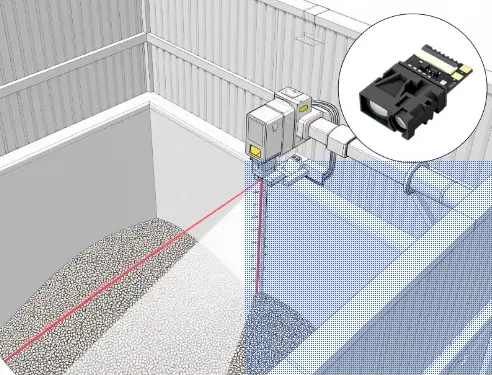
A ToF sensor calculates distance by measuring the time it takes for a laser pulse to travel to an object and back.
Most industrial ToF sensors—such as Meskernel’s long-range laser distance sensors (5–2000 m)—use pulsed ToF for maximum accuracy and outdoor performance.
LiDAR systems also use time-of-flight, but they employ more complex scanning optics, rotating mirrors, or solid-state VCSEL arrays to generate a multi-point or full-area point cloud.
In short:
- ToF sensor = single-point or small-array measurement
- LiDAR = multi-point or full-area scanning
Scanning vs. Single-Point Measurement
ToF distance sensors are typically single-point, delivering fast, stable, high-frequency distance data—ideal for real-time control loops such as:
LiDAR is designed for area scanning, providing:
- 2D or 3D point clouds
- Mapping & SLAM
- Navigation & localization
- Wide field-of-view sensing
Side-by-Side Comparison Table
| Feature | ToF Sensor (Single-Point) | LiDAR (Scanning System) |
|---|
| Range | Short–long range (0.1–2000 m depending on model) | Medium–long range (5–300 m typical) |
| Accuracy | High accuracy (±1–10 mm typical for industrial modules) | Moderate–high accuracy; depends heavily on scanning method and reflectivity |
| Cost | Low to medium; ideal for OEM modules | Higher due to optics, scanning units, or solid-state arrays |
| Size | Very compact; PCB or small metal housing | Larger, especially rotating LiDAR |
| Outdoor Performance | Excellent on long-range pulsed ToF models; strong sunlight immunity | Often reduced under sunlight, rain, fog, or snow |
| Power Consumption | Very low | Medium to high |
| Best Use Case | Height sensing, distance control, level measurement, UAV ranging | Mapping, SLAM, autonomous navigation, robotics perception |
| Data Output | Single distance value (high frequency) | Full point cloud (2D/3D) |
When to Choose a ToF Sensor
A ToF distance sensor is the best choice when your application needs fast, precise single-point measurement rather than full scanning.
✔ Choose ToF if your project needs:
- High-frequency distance feedback (up to 1–10 kHz depending on module)
- Long-range measurement (up to 2000 m with our pulsed ToF OEM modules)
- Compact size for drones, robots, or embedded devices
- Strong outdoor performance under sunlight
- Stable measurement on low-reflectivity targets
- Low power consumption
- Lower cost than LiDAR
Common industrial applications:
- UAV altitude hold / terrain following
- AGV/AMR distance control
- Smart warehouses
- Conveyor-based material detection
- Industrial positioning systems
- Tank/level measurement
- Distance-trigger systems
- Machine automation & safety
Meskernel’s industrial laser distance sensor modules are widely used in UAV mapping, robotics, smart agriculture, mining, and factory automation.




When LiDAR Is the Better Choice
LiDAR is ideal for applications requiring wide-area perception, environmental awareness, or 3D mapping.
✔ Choose LiDAR if your project needs:
- Obstacle detection across a wide field of view
- SLAM navigation
- 2D or 3D mapping
- Spatial perception instead of just distance feedback
- Large area scanning for autonomous systems
Best-fit applications:
- Autonomous mobile robots
- Driverless forklifts & self-driving vehicles
- Surveying & terrain mapping
- Forestry 3D scanning
- Environmental monitoring
- Large-area security systems
Hybrid Systems (ToF + LiDAR)
Many advanced systems combine both ToF and LiDAR, taking advantage of each technology’s strengths.
Example hybrid configuration:
- LiDAR → Builds a map, detects obstacles
- ToF sensor → Provides precise height or distance feedback for control loops
Benefits of hybrid sensing:
- Higher reliability
- Redundancy for mission-critical tasks
- Improved performance under low reflectivity or sunlight
- Better measurement stability
Common hybrid use cases:
- UAV terrain mapping + real-time altitude hold
- AMR navigation + dock alignment
- Smart agriculture robots
- Industrial inspection platforms
FAQ for ToF Sensor vs LiDAR
-
What is the main difference between a ToF sensor and LiDAR?
A ToF sensor measures a single point distance, while LiDAR scans multiple points to create a 2D or 3D map.
ToF sensors are ideal for precise point measurement; LiDAR is ideal for mapping and navigation.
-
Is a ToF sensor cheaper than LiDAR?
Yes. ToF distance sensors are significantly more cost-effective because they do not require complex scanning optics or rotating mirrors. This makes them the preferred choice for OEM manufacturers, UAVs, robotics, and industrial automation systems.
-
Can ToF sensors work outdoors under strong sunlight?
Industrial pulsed ToF laser modules—such as those used in long-range Meskernel sensors—offer excellent sunlight immunity, making them suitable for UAV flight, mining, forestry, and outdoor automation.
-
Does LiDAR provide better accuracy than ToF?
Not always.
High-quality ToF distance sensors can achieve ±1–10 mm accuracy, even at long ranges. LiDAR accuracy depends on scanning type and is often similar or slightly lower at long distances.
-
Which should I use for drones—ToF or LiDAR?
Use ToF for:
Altitude hold
Landing assistance
High-speed distance control
Use LiDAR for:
Navigation
Obstacle mapping
Environmental perception
Many drone manufacturers use both for maximum reliability.
-
Which technology is better for industrial automation?
For single-point measurement, ToF sensors are more stable, cost-effective, and precise.
For mapping or area scanning, LiDAR is preferred.
Compare Industrial ToF & LiDAR Models
Meskernel offers a full portfolio of industrial-grade laser distance sensors, including:
- Short-, medium-, and long-range ToF distance sensors (5–2000 m)
- OEM laser distance measurement modules for integrators
- Outdoor/high-sunlight pulsed ToF sensors
- Precision measurement modules for UAVs, robotics, and automation
👉 Explore our ToF & LiDAR-compatible distance sensors
👉 Request OEM samples now
👉 Download datasheets and integration guides
https://meskernel.net/time-of-flight-distance-sensor/