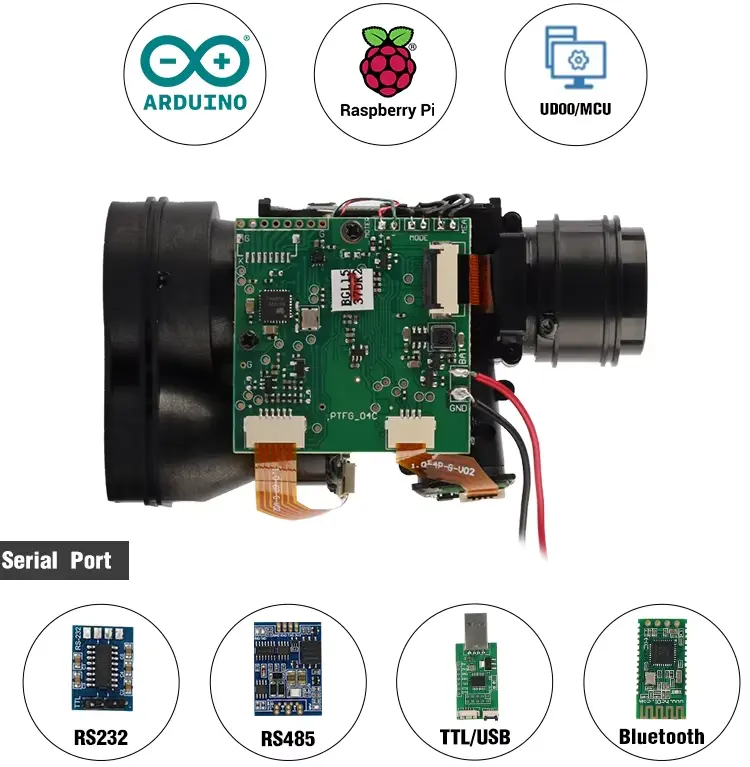
When engineers start building a laser-based sistema de medición de distancias, one common question comes up very early:
Should I use Raspberry Pi or Arduino to connect my laser sensor?
This question becomes even more important when the project involves long-range distancia láser sensors, higher accuracy, or potential OEM and industrial deployment. In this article, we compare laser sensor for Raspberry Pi vs Arduino from a practical engineering perspective, focusing on real-world medición láser systems rather than hobby experiments.
Why This Comparison Matters for Laser Measurement Projects
Both Raspberry Pi and Arduino are widely used in medición de la distancia projects, but sensores láser are fundamentally different from ultrasonic or infrared modules.
A professional laser sensor de distancia:
- Performs internal signal processing
- Outputs ready-to-use distance data
- Often communicates via UART, RS485, or RS232
- Is designed for long-range, high-accuracy, medición sin contacto
Because of this, the choice of controller platform has a direct impact on system stability, scalability, and integration cost.
Hardware Overview: Raspberry Pi vs Arduino
| Característica | Raspberry Pi | Arduino |
|---|
| Operating system | Linux-based | Bare-metal / RTOS |
| Processing power | Alta | Low to moderate |
| Interfaces | UART, USB, Ethernet, RS485 (via adapter) | UART, I2C, SPI |
| Data handling | Excellent | Limited |
| Best suited for | Complex systems, data processing | Simple control tasks |
From a laser measurement standpoint, neither platform measures distance directly. The laser sensor does the measurement; the platform only reads and processes the data.
Laser Sensor for Raspberry Pi: Strengths and Limitations
Using a laser sensor for Raspberry Pi is a common choice for engineers working on long-range or high-accuracy projects.
Ventajas clave:
- Stable serial communication with industrial sensores láser de distancia
- Easy integration of UART / RS485 telémetro láser modules
- Powerful data processing, filtering, and logging
- Built-in networking for remote monitoring and cloud integration
Because Raspberry Pi runs Linux, it is especially suitable for:
- Long-range laser rangefinder systems
- Multi-sensor fusion
- OEM prototyping
- Industrial gateways and edge devices
Limitaciones:
- Not ideal for strict real-time control
- Higher power consumption than Arduino
For most long-range laser measurement systems, these limitations are rarely critical.
Arduino Distance Measurement: When Does It Make Sense?
Arduino is often associated with distance sensor projects, but its strengths lie in simplicity, not complexity.
Arduino works well when:
- The laser sensor is short-range
- Measurement speed is low
- The system requires simple triggering or control
- Power consumption must be minimal
However, Arduino becomes less suitable when:
In practice, Arduino is more common in educational or proof-of-concept projects rather than production laser measurement systems.

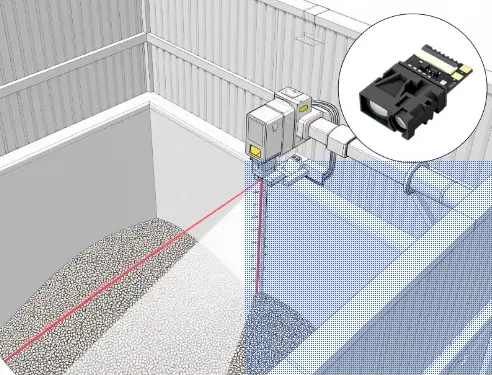
Which Platform Do Engineers Choose for Long-Range Laser Sensors?
For sensores láser de distancia de largo alcance, engineers typically choose Raspberry Pi over Arduino.
The reason is simple:
- Long-range laser sensors already handle precise óptico measurement internally
- Raspberry Pi excels at receiving, processing, storing, and transmitting measurement data
- Industrial laser rangefinder modules are designed to work with UART or RS485, not GPIO-level timing
This makes Raspberry Pi a more natural match for:
- Pulse laser rangefinder modules
- High-precision phase-based laser sensors
- OEM laser measurement solutions
Application Comparison: Raspberry Pi vs Arduino
Robotics & AGV
- Raspberry Pi: Preferred for navigation, mapping, and data fusion
- Arduino: Limited to basic triggering
UAV & Drones
- Raspberry Pi: Suitable for long-range altitude and obstacle measurement
- Arduino: Rarely used with professional laser rangefinders
Construcción y topografía
- Raspberry Pi: Common choice for long-range laser measurement systems
- Arduino: Not suitable for high-accuracy topografía
Automatización industrial
- Raspberry Pi: Used as an edge controller or gateway
- Arduino: Used only for simple I/O tasks





Final Verdict: Raspberry Pi or Arduino for Laser Sensors?
If your project involves:
- Long-range measurement
- Alta precisión
- Non-contact optical sensing
- Industrial or OEM applications
Then Raspberry Pi is the better platform for integrating a laser distance sensor.
Arduino still has its place in simple control and educational projects, but for professional laser measurement systems, Raspberry Pi provides the flexibility, stability, and scalability engineers need.
Choosing the Right Laser Sensor Matters More Than the Platform
No matter which platform you choose, the laser sensor itself plays the most critical role in system performance.
Industrial-grade laser distance sensors:
- Perform accurate distance calculation internally
- Output stable digital data
- Are designed for long-term reliability
If you are evaluating a laser sensor for Raspberry Pi or Arduino, selecting a proven módulo sensor láser de distancia will significantly reduce development risk and integration time.
Choosing the Right Meskernel Laser Sensor for Raspberry Pi or Arduino
When building a laser measurement system, the choice of laser sensor module matters more than the platform itself. While Raspberry Pi and Arduino provide different levels of computing power and integration convenience, your sensor selection determines the achievable range, precision, and reliability.
Below are several recommended Meskernel laser sensor models that fit common project categories—from DIY to industrial and OEM systems:
- Best for: Long-range measurement (up to 2000 m), industrial monitoring, high-altitude robotics, surveying
- Why it works:
- Long measuring range (5 m–2000 m)
- Reliable for non-contact distance measurement over large distances
- UART/RS485/RS232 interfaces allow easy connection with Raspberry Pi or Arduino via adapter
- Recommended platform: Raspberry Pi, especially for projects needing networking, data logging, or cloud integration
- Typical uses: UAV altitude sensing, large-area distance measurement, industrial site monitoring
👉 If your application prioritizes long distance and stable performance, this is one of the best choices for a laser sensor for Raspberry Pi.
- Best for: Short-to-mid-range high-accuracy use cases (0.03 m–100 m)
- Why it works:
- Millimeter-level accuracy (±1 mm + D/10000)
- Red or green laser beam options, with green providing better visibility under bright conditions
- Supported interfaces: USART, RS485, RS232
- Recommended platform: Both Raspberry Pi and Arduino
- For data logging and advanced processing, use Raspberry Pi
- For simple trigger-response or embedded control, Arduino can suffice
- Typical uses: Industrial automation, robotics precision tasks, distance-feedback control systems
👉 These sensors are perfect when precision is the core requirement, and your choice of platform can be based on how much data processing / IoT integration you need.
- Best for: High-speed measurement and extended range (up to 3000 m)
- Why it works:
- High measurement frequency
- Supports rapid distance updates
- Multiple form factors (cylindrical, square, telescope)
- Solid stability for motion-rich environments
- Recommended platform: Raspberry Pi, especially when combining with advanced navigation, mapping, or AI algorithms
- Typical uses: Autonomous robotics, terrain scanning, UAV-based surveying
👉 For projects where measurement frequency, reliability, and automation matter the most, PTFS series sensors shine when paired with Raspberry Pi.
🛠 Integration Notes (Raspberry Pi vs Arduino)
| Tipo de sensor | Best Platform | Razón |
|---|
| TS1224-Mini | Raspberry Pi | Needs high-level data handling and possibly remote monitoring |
| Sensores láser de fase | Pi or Arduino | Arduino works if only basic control is needed; Pi adds flexibility |
| PTFS Pulse Sensors | Raspberry Pi | High-frequency data and system logic benefit from Pi’s processing |
- Arduino: good for simpler, educational, or lower-cost short-range systems
- Raspberry Pi: generally better for professional-grade, data-rich, industrial, or OEM projects
🔎 Quick Decision Guide
- Do you need long-range with networking or logging? → TS1224 + Raspberry Pi
- Do you need millimeter accuracy in tight spaces? → Phase Laser Sensor with Raspberry Pi or Arduino
- Do you need fast, repeated distance measurement? → PTFS Series + Raspberry Pi
- Is your priority cost + simplicity? → Phase Laser on Arduino for basic use
📌 Wrap-Up
Choosing between Raspberry Pi vs Arduino is only part of the equation.
More importantly, you must select a laser sensor that matches your performance goals. Meskernel’s product portfolio—from TS1224 to Phase and PTFS series—covers the full spectrum of applications:
✅ Industrial automation
✅ Robotics and autonomous systems
✅ UAV surveying and mapping
✅ OEM product integration
Combine the right sensor with the right platform to achieve optimal performance and reliability.
Comparison FAQ: Raspberry Pi vs Arduino for Laser Sensors
-
Is Raspberry Pi better than Arduino for laser distance sensors?
-
Which is more accurate: Raspberry Pi or Arduino for distance measurement?
Accuracy does not depend on Raspberry Pi or Arduino themselves, but on the laser sensor module used.
However, Raspberry Pi is better suited for high-accuracy laser sensors because it can reliably handle:
Higher data rates
Advanced filtering
Long-term data storage
This makes Raspberry Pi more practical for millimeter-level laser distance measurement.
👉 Full explanation available in this comparison article.
-
Can Arduino be used with long-range laser rangefinders?
Arduino can technically connect to long-range laser rangefinders via UART, but it is not ideal for most long-range applications.
Long-range laser sensors often require:
Stable serial communication
Data buffering
Advanced processing
These requirements are better handled by Raspberry Pi, as explained in our Raspberry Pi vs Arduino laser sensor comparison.
-
Laser sensor for Raspberry Pi vs Arduino: which is better for OEM projects?
For OEM and industrial projects, Raspberry Pi is usually the better platform.
OEM projects often involve:
Multiple sensors
Communication with other systems
Data visualization or remote access
Raspberry Pi provides a faster development path and lower integration risk when working with industrial laser distance sensor modules.
-
Which platform is easier to integrate with industrial laser sensors?
Raspberry Pi is easier to integrate with industrial laser sensors because most professional módulos telémetro láser output data via:
UART
RS485
RS232
Raspberry Pi supports these interfaces naturally through adapters and Linux drivers, while Arduino may require additional development and optimization.
-
Should I start with Arduino or Raspberry Pi for laser sensor prototyping?
For simple educational or short-range projects, Arduino is a good starting point.
For projects involving:
Long-range laser measurement
High precision
Future industrial or OEM deployment
Starting with Raspberry Pi is more efficient and avoids redesign later.
This decision is discussed in detail in our Raspberry Pi vs Arduino laser sensor guide.
-
Does Raspberry Pi replace Arduino in laser measurement systems?
No. Raspberry Pi and Arduino serve different roles.
Arduino is suitable for simple control tasks
Raspberry Pi excels at system integration and data processing
In many professional laser measurement systems, Raspberry Pi is used as the main controller, while Arduino may still handle auxiliary I/O tasks.
https://meskernel.net/time-of-flight-distance-sensor/