Common Problems and Practical Troubleshooting Guide
Serial communication issues are among the most frequent problems engineers encounter when integrating a laser capteur de distance into real-world systems.
Whether you are testing a module de capteur de distance laser on a workbench, connecting it to a microcontroller, PLC, UAV flight controller, or industrial controller, a single wiring mistake or configuration mismatch can cause the sensor to appear completely unresponsive.
This article summarizes the most common serial communication problems encountered during distance laser sensor connection and testing, and provides practical, step-by-step troubleshooting guidance based on real integration experience.
Why Serial Communication Problems Are Common in Laser Distance Sensors
Détecteurs de distance à laser are widely used in industrial automation, robotics, UAVs, arpentage equipment, and monitoring systems. Most of these applications rely on serial interfaces such as UART (TTL) or RS485 for data transmission.
Serial communication problems usually do not indicate a faulty sensor. In most cases, the root cause is related to:
- Wiring details
- Serial parameter mismatch
- Power supply instability
- Controller compatibility
- Electrical noise or grounding issues
Understanding these factors can significantly reduce debugging time.
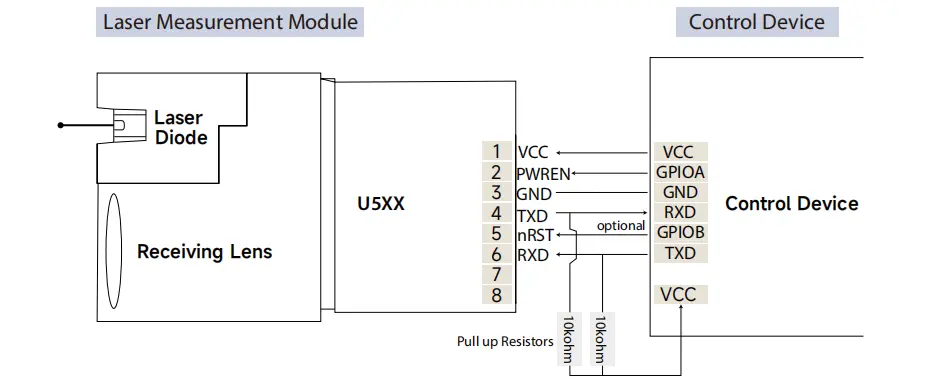
1. No Common Ground Between Devices
One of the most overlooked causes of serial communication failure is the absence of a common ground.
Serial signals require a shared reference voltage. If the capteur de distance laser and the host device (PC, MCU, PLC, or flight controller) do not share the same ground, the signal levels cannot be interpreted correctly.
Typical symptoms:
- Sensor is powered on
- Serial port opens normally
- No data is received
Troubleshooting tips:
- Always connect Sensor GND ↔ Host GND
- Pay special attention when using USB-to-serial adapters or separate power supplies
2. Serial Parameters Do Not Match
Both communication sides must use exactly the same serial configuration.
Common parameters that must match:
- Baud rate
- Data bits
- Stop bits
- Parity
Typical laser distance sensor configuration:
Baud rate: 115200
Data bits: 8
Stop bits: 1
Parity: None
Always verify the correct parameters in the sensor datasheet and ensure the host software or controller is configured accordingly.
3. TX / RX Wiring or Interface Type Errors
Incorrect wiring is another frequent issue.
Common mistakes:
- TX connected to TX
- RX connected to RX
- TTL device connected directly to an RS232 port
Correct wiring:
- Sensor TX → Host RX
- Sensor RX → Host TX
Important note:
TTL (UART) and RS232 use different voltage levels. Connecting them directly may cause communication failure or hardware damage.
4. Cable Quality, Length, and EMI Interference
Cable issues can cause unstable or unreliable communication, especially in industrial or outdoor environments.
Typical symptoms:
- Communication works with short cables but fails with longer ones
- Data drops or becomes corrupted intermittently
Recommendations:
- Use shielded cables in noisy environments
- Keep cable length as short as possible
- Prefer RS485 for long-distance or industrial applications
5. Device Compatibility and Controller Differences
In some cases, the same laser distance sensor works with one controller but not with another.
Common scenarios:
- Works with one display module but not another
- Works on one PC but fails on a different PC
- Works with one MCU but not with another
These issues are often caused by differences in serial timing, buffer handling, or protocol implementation.
Solution :
- Check the controller’s serial specifications
- Confirm compatibility with the sensor manufacturer if necessary
6. Data Errors or Garbled Output
Incorrect or corrupted data is often caused by:
- Baud rate mismatch
- Electrical interference
- Unstable grounding or power supply
Troubleshooting steps:
- Double-check baud rate settings
- Reduce baud rate for testing
- Improve grounding and shielding
7. Grounding Requirements Change After Hardware Replacement
Sometimes serial communication works in the original setup but fails after replacing a controller, power supply, or display.
This is usually caused by different electrical reference designs or isolation methods.
Recommendation:
- Re-evaluate grounding strategy after hardware changes
- Use RS485 with isolation for industrial systems when possible
8. Use Loopback Testing for Fast Diagnosis
Loopback testing is an efficient way to determine whether the serial port itself is working.
How it works:
- Short TX and RX pins on the serial port
- Send data from the host
- Check if the same data is received
If loopback works, the issue is likely external to the serial port hardware.
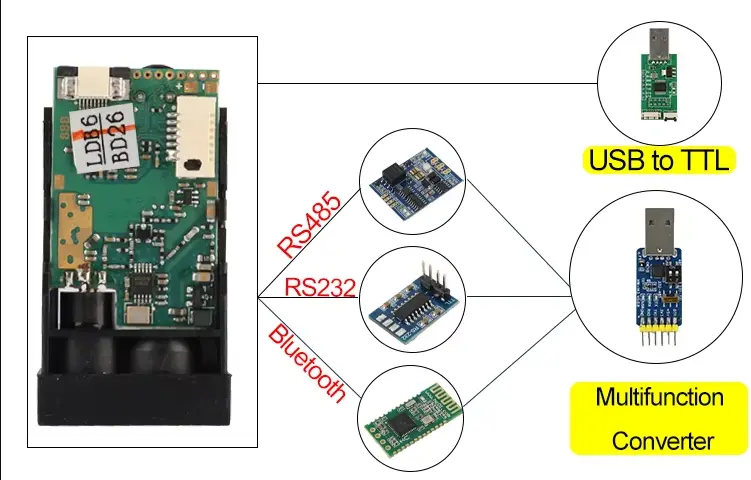
9. USB-to-Serial Driver Issues
When using USB-to-serial adapters, driver problems are common.
Common chipsets:
Troubleshooting tips:
- Confirm the correct driver is installed
- Check for device errors in the system device manager
- Try a different USB port or adapter
10. Serial Port Occupied by Other Software
If another program is using the same serial port, communication will fail.
Check for:
- Background monitoring tools
- Debug software
- Previously opened serial terminals
Ensure only one application accesses the serial port at a time.

11. Power Supply Instability
Détecteurs de distance à laser may draw higher current during startup or measurement.
Symptoms:
- Intermittent communication
- Measurement data drops or freezes
Recommendations:
- Verify voltage and current ratings
- Avoid powering sensors directly from weak USB ports
- Use a stable, regulated power supply
12. MCU Firmware or Host Software Issues
Sometimes the issue lies in the software rather than the hardware.
Common problems:
- Receive buffer overflow
- Incorrect frame parsing
- Serial listener not running continuously
Best practice:
- Test the sensor first using a serial terminal tool
- Confirm stable output before integrating into firmware or applications
Recommended Troubleshooting Order
To debug serial communication efficiently, follow this sequence:
- Confirm common ground
- Verify serial parameters
- Check TX / RX wiring and interface type
- Perform loopback testing
- Inspect cables and power supply
- Investigate software and protocol handling
Final Thoughts
Serial communication problems with laser distance sensors are rarely caused by defective hardware. In most cases, they result from wiring, configuration, grounding, or compatibility issues.
A structured troubleshooting approach can save hours of debugging time and prevent unnecessary component replacement.
If you are testing a module de capteur de distance laser and experiencing unstable or missing serial output, providing details such as interface type, baud rate, controller model, power supply, and wiring method will greatly accelerate problem diagnosis.
Frequently Asked Questions About Serial Communication in Laser Distance Sensors
-
What is serial communication in a laser distance sensor?
Serial communication in a laser distance sensor refers to the method used to transmit measurement data between the sensor and a host device such as a PC, microcontroller, PLC, or flight controller.
Common serial interfaces include UART (TTL) et RS485, which send data sequentially over TX and RX lines.
-
Why does my laser distance sensor have no serial communication output?
A laser distance sensor may have no serial communication output due to mismatched baud rate settings, missing common ground, incorrect TX/RX wiring, unstable power supply, or the serial port being occupied by another application.
These issues are more common than hardware failure and should be checked first.
-
How do I troubleshoot serial communication problems step by step?
To troubleshoot serial communication problems, follow this order:
1.Confirm the sensor and host share a common ground
2.Verify baud rate and serial parameters
3.Check TX and RX wiring
4.Perform a loopback test on the serial port
5.Inspect power supply stability and cable quality
6.Review firmware or host software configuration
This method helps isolate the root cause efficiently.
-
What serial communication parameters are required for laser distance sensors?
Most laser distance sensors use standard serial communication parameters such as:
8 data bits
1 stop bit
No parity
The baud rate varies by model and must match exactly on both the sensor and host device. Always check the sensor datasheet before configuration.
-
Why does serial communication work on one controller but not another?
Serial communication may work on one controller but fail on another due to differences in serial timing, buffer handling, voltage levels, or protocol implementation.
Even when baud rates match, some controllers handle serial data differently, affecting compatibility.
-
Is RS485 better than UART for serial communication?
Oui, RS485 serial communication is generally more robust than UART (TTL), especially for long cable runs, industrial environments, or electrically noisy applications.
RS485 supports differential signaling, better noise immunity, and longer transmission distances.
-
Can a missing ground cause serial communication failure?
Yes. A missing or unstable ground connection is a very common cause of serial communication failure.
Without a shared reference voltage, the host device cannot correctly interpret serial signal levels, even if TX and RX are wired correctly.
-
How does power supply affect serial communication reliability?
An unstable or insufficient power supply can cause serial communication issues such as intermittent data loss, corrupted frames, or complete communication failure.
Laser distance sensors may draw higher current during startup or measurement cycles, making stable power essential.
-
What is a loopback test in serial communication?
A loopback test is a diagnostic method used to verify whether a serial port is functioning correctly.
By shorting the TX and RX pins and sending data, the host should receive the same data back. If it does, the serial port hardware and driver are working properly.
-
Can USB-to-serial adapters cause serial communication problems?
Yes. USB-to-serial adapters can cause serial communication issues due to driver problems, chipset incompatibility, or unstable USB power.
Using reliable chipsets such as FTDI or properly installed drivers for CH340 or CP2102 adapters can improve stability.
-
How can I improve serial communication stability in industrial applications?
To improve serial communication stability:
Use RS485 instead of TTL
Keep cables short or use shielded cables
Ensure proper grounding
Use isolated interfaces when possible
Avoid sharing power with high-noise equipment
These practices significantly reduce communication errors.
https://meskernel.net/oem-laser-distance-sensor/