레이저 이해 거리 센서 작동 원리는 자동화, 로봇 공학 또는 측정 시스템을 다루는 엔지니어, 개발자 및 시스템 통합자에게 필수적입니다. 이 문서에서는 다음과 같은 방법을 설명합니다. 레이저 거리 센서는 세 가지 주요 원칙으로 작동합니다: 비행 시간(ToF), 위상 시프트, 및 삼각 측량. 또한 프로젝트에 가장 적합한 유형을 선택하는 데 도움이 되는 실제 적용 예시도 제공합니다.
📌 레이저 거리 센서란 무엇인가요?

A 레이저 거리 센서 는 레이저 빔을 사용하여 물체까지의 거리를 측정하는 비접촉식 디바이스입니다. 레이저 신호를 방출하고 대상에서 반사되는 레이저 신호를 감지한 후 특정 측정 원리를 사용하여 거리를 정확하고 빠르게 계산합니다. 핵심 기능은 레이저 거리 센서의 작동 원리에 따라 달라지며, 센서 유형과 용도에 따라 달라집니다.
⚙️ 1. 비행 시간(ToF): 핵심 레이저 거리 센서 작동 원리
레이저 거리 센서의 작동 원리
센서는 짧은 레이저 펄스를 방출하고 반사된 신호가 물체에서 돌아오는 데 걸리는 시간을 측정합니다.
🧠 거리 = (광속 × 비행 시간) ÷ 2
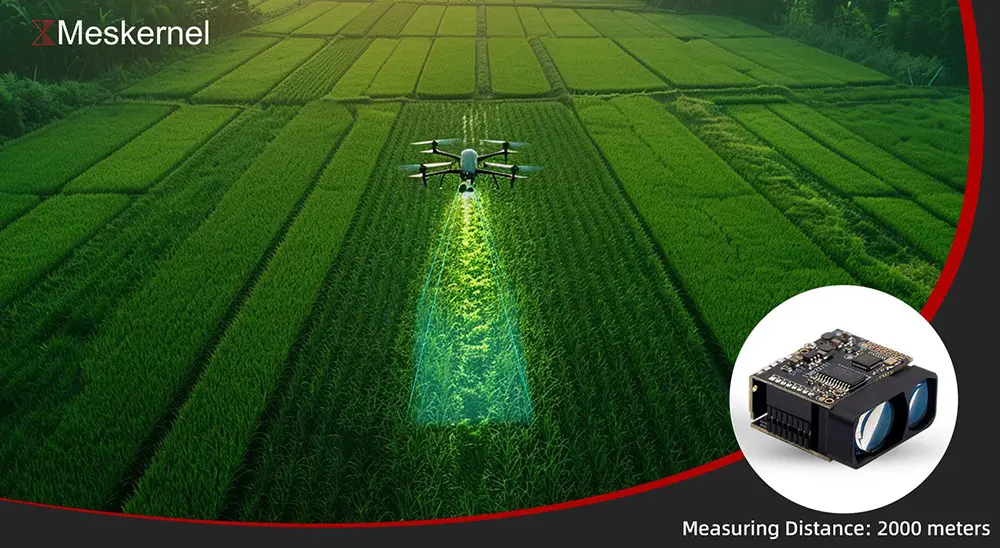
이는 장거리 애플리케이션에서 가장 일반적인 레이저 거리 센서 작동 원리입니다.
장점
- 장거리 측정에 이상적(최대 2000m)
- 고속 작동, 움직이는 목표물에서도 잘 작동합니다.
- 실외 환경에서도 안정적인 성능 제공
애플리케이션
- UAV/드론
- 스마트 교통 시스템
- 산업 거리 모니터링
- 장거리 개체 탐지


⚙️ 2. 위상 편이: 고정밀 레이저 거리 센서의 작동 원리
작동 방식
센서가 변조된 레이저 빔을 방출하고 방출된 신호와 수신된 신호의 위상차를 비교하여 거리를 계산합니다.
위상 이동은 레이저 파의 이동 거리와 직접적인 상관관계가 있습니다.
이 레이저 거리 센서의 작동 원리는 정밀도 때문에 산업 자동화 분야에서 선호됩니다.
장점
- 단거리에서 중거리까지 매우 정확함
- 다양한 환경 조건에서 안정성 향상
애플리케이션
- 자재 관리 시스템
- 공장 자동화
- 컨베이어 모니터링
- 실내 레벨 감지



⚙️ 3. 삼각 측량: 단거리 레이저 거리 센서의 작동 원리
작동 방식
삼각 측량은 기하학을 사용합니다. 센서가 레이저 포인트를 대상에 투사하면 반사된 빔이 위치 감지 검출기(PSD)에 의해 알려진 각도로 캡처됩니다. PSD에서 반사되는 위치는 거리에 따라 달라집니다.
이 레이저 거리 센서의 작동 원리는 컴팩트한 크기와 정밀도가 중요한 임베디드 시스템에서 널리 사용됩니다.
장점
- 고해상도, 단거리 측정에 탁월함
- 매우 빠른 응답 시간
- 컴팩트하고 저전력
애플리케이션
- 모바일 로보틱스(물체 회피)
- 스마트폰(예: 얼굴 인식)
- 의료 기기
- 임베디드 OEM 시스템
📊 레이저 거리 센서 작동 원리 비교하기
| 작동 원리 | 범위 | 정확성 | 속도 | 모범 사용 사례 |
|---|
| ToF | 1-2000m+ | ±1m | 높음 | 실외/산업 현장의 장거리 작업 |
| 위상 시프트 | 0.01-200m | ±3mm | Medium | 실내 자동화 및 물류 |
| 삼각 측량 | 0.01-1m | ±0.1mm | 매우 높음 | 로봇 공학, 스마트폰, 임베디드 도구 |
이러한 차이점을 이해하면 요구 사항을 올바른 레이저 거리 센서 작동 원리에 맞출 수 있습니다.
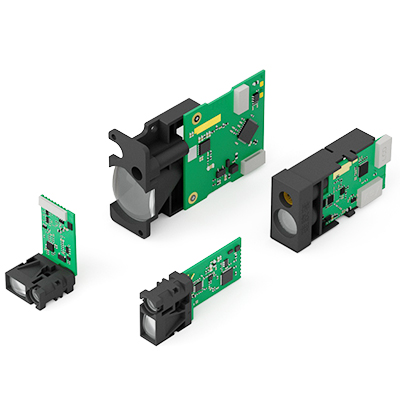
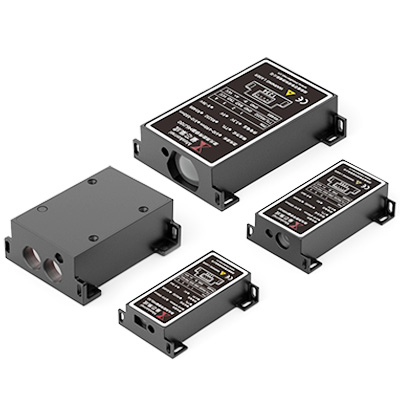
이러한 원리를 이용한 실제 레이저 거리 센서 예시
메커널 고품질 제공 레이저 거리 모듈 위에서 언급한 각 원칙을 기반으로 구축되었습니다:
- ✅ LDJ-4Hz 및 10Hz 시리즈 - 단거리 및 중거리 산업 작업에 위상 시프트 사용
- ✅ TC25 & TS1224 시리즈 - 최대 2000m의 장거리 측정을 위해 ToF를 활용하세요.
- ✅ OEM 미니 모듈 - 공간에 민감한 애플리케이션용
올바른 레이저 거리 센서 작동 원리를 선택하면 시스템의 신뢰성과 정확성을 극대화할 수 있습니다.



👉 모든 레이저 거리 센서 살펴보기 "
레이저 거리 센서 작동 원리에 대한 FAQ
Q1: 드론에 가장 적합한 레이저 거리 센서 작동 원리는 무엇인가요?

ToF는 장거리 기능과 모션 관련 오류에 대한 저항성으로 인해 가장 신뢰할 수 있습니다.
Q2: 실내에서 사용하기에 위상변환이 ToF보다 낫나요?
예, 위상 시프트는 더 짧은 거리에서 더 높은 해상도를 제공하여 실내 자동화에 이상적입니다.
Q3: 삼각 측량과 ToF의 차이점은 무엇인가요?
삼각 측량은 지오메트리를 기반으로 하며 근거리 감지에 사용되는 반면, ToF는 레이저 이동 시간에 의존하며 장거리 감지에 적합합니다.
Q4: 한 공급업체에서 세 가지 유형의 센서를 모두 구할 수 있나요?
예. 다음과 같은 플랫폼 메커널 모든 주요 레이저 거리 센서 작동 원리에 기반한 센서를 제공합니다.
그리고 레이저 거리 센서 어떤 작동 원리를 선택하느냐에 따라 프로젝트의 성능, 비용, 안정성에 큰 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다. 고정밀 로봇 시스템을 설계하든, 견고한 실외 거리 추적기를 설계하든, 다음과 같은 원리를 이해해야 합니다. 레이저 센서 작업은 올바른 솔루션을 선택하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
비행 시간, 위상 이동 및 삼각 측량의 기본 사항을 숙지하면 정보에 입각한 의사 결정을 내리고 배포할 수 있습니다. 레이저 거리 센서 더 효과적으로 사용할 수 있습니다.
https://meskernel.net/time-of-flight-distance-sensor/