Ao escolher um sensor de distância for industrial or automation projects, one of the most important decisions is whether to use an análogo distance sensor or a digital distance sensor.
Both technologies measure distance accurately, but they differ in signal tipo de saída, precision, and integration method.
This article will explain how each works, compare their advantages and limitations, and help you decide which sensor type best fits your application — from industrial automation to robotics and level measurement.
What Is a Distance Sensor?

A distance sensor measures the distance between the sensor and a target object using technologies such as laser triangulation, infrared reflection, or tempo de voo (ToF).
Depending on the output method, the measured distance is transmitted either as a continuous analog signal or as digital data.
Analog Distance Sensors: Continuous and Flexible
Como funcionam
An analog distance sensor provides a continuous output, such as a 0–10 V voltage or 4–20 mA current, that changes in proportion to the distance measured.
Controllers, PLCs, and analog input modules can read this signal directly.
Vantagens
- ✅ Continuous feedback for smooth motion control
- ✅ Simple integration with PLCs or analog I/O modules
- ✅ Fast signal response with no data decoding
- ✅ Cost-effective for basic process control tasks
Limitações
- ⚠️ Susceptible to electrical noise over long cable runs
- ⚠️ Limited precision due to signal fluctuation
- ⚠️ Potential calibration drift over time
Melhor para:
Real-time level control, process automation, and feedback loops in stable environments.
👉 Exemplo: 4–20mA laser distance sensor modules
Digital Distance Sensors: Smart and Noise-Resistant
Como funcionam
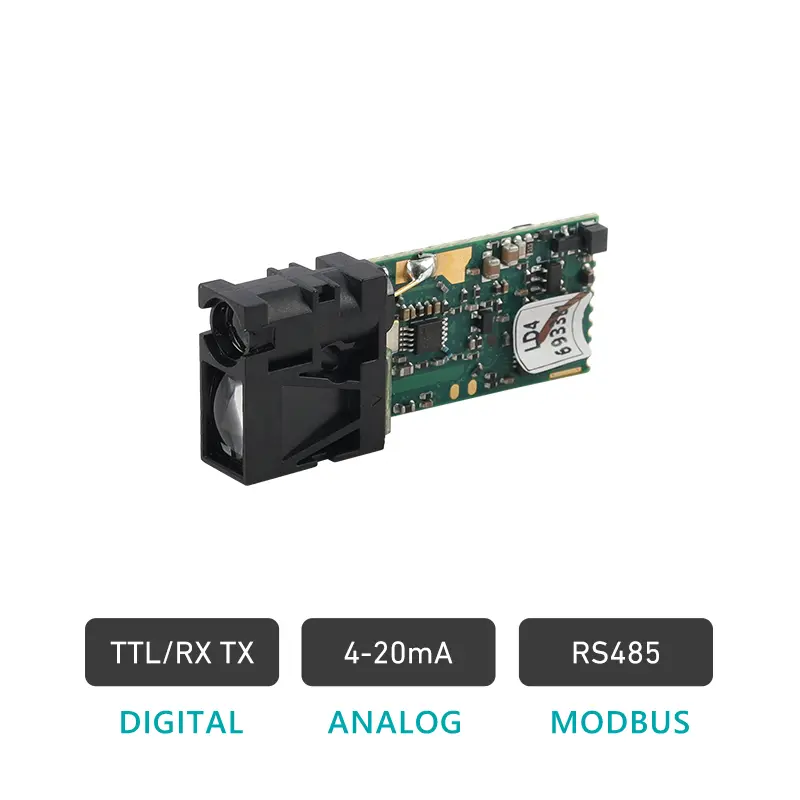
A digital distance sensor converts measurement results into discrete digital data, which can be transmitted through interfaces like UART, RS485 (Modbus), or I²C.
This signal represents an exact numeric value instead of a continuous waveform.
Vantagens
- ✅ High accuracy and strong resistance to electrical noise
- ✅ Long-distance communication over industrial networks
- ✅ Multiple output protocols (UART, RS485, Modbus, I²C)
- ✅ Easy integration with microcontroladores and smart devices
Limitações
- ⚠️ Requires digital communication setup
- ⚠️ Slightly slower update rate due to serial data transfer
- ⚠️ May need converters (e.g., RS485-to-USB) for testing
Melhor para:
Industrial automation, robotics, AGVs, and smart systems requiring reliable and interference-free data.
👉 Explore: RS485 digital distance sensor modules
Key Differences Between Analog and Digital Distance Sensors
| Caraterística | Analog Distance Sensor | Digital Distance Sensor |
|---|
| Tipo de saída | Voltage (0–10V) or Current (4–20mA) | UART, RS485, or Binary Signal |
| Noise Resistance | Baixa | Elevado |
| Precisão | Moderado | Elevado |
| Signal Transmission | Limited distance | Long-distance (network capable) |
| Setup | Plug-and-play | Protocol configuration needed |
| Integration | PLCs and analog controllers | Microcontrollers and automation networks |
| Tempo de resposta | Muito rápido | Fast, but protocol-dependent |
| Ideal Application | Process control, level measurement | Robotics, automation, IoT systems |
How to Choose the Right Sensor for Your Application
Choosing between analog and digital distance sensors depends on your system design, accuracy requirements, and environment.





Choose an Analog Distance Sensor if:
- You need continuous feedback for motion or level control.
- Your system supports analog voltage or 4–20 mA input.
- You have short cable runs and minimal electrical interference.
Choose a Digital Distance Sensor if:
- You need high precision and data stability.
- Your installation involves long cable distances or noisy environments.
- You use microcontrollers, PLCs, or smart controllers supporting RS485 or UART.
Real-World Examples
- Factory automation: Digital RS485 sensors ensure stable distance monitoring in conveyor or packaging systems.
- Tank level control: Analog sensors provide continuous liquid-level measurement for process regulation.
- Robotics and AGV navigation: ToF-based digital sensors with UART or I²C ensure accurate real-time distance deteção.
Dual-Output Laser Distance Sensors
Moderno módulos de sensores de distância por laser often combine both digital and analog outputs — such as RS485 + 4–20 mA or UART + voltage output.
This allows engineers to integrate one sensor model across multiple systems.
👉 Ver o nosso dual-output laser distance sensor modules for flexible OEM integration.
FAQs: Analog vs Digital Distance Sensors
Q1. What’s the difference between analog and digital distance sensors?
Analog sensors output a continuous voltage or current signal that varies with distance.
Digital sensors send exact distance data via serial communication (e.g., UART or RS485).
Q2. Which provides higher accuracy?
Digital distance sensors generally offer higher precision and better noise immunity, especially in industrial environments with long wiring.
Q3. Can I convert an analog sensor to a digital one?
Not directly — but you can use an ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) to digitize an analog signal for a microcontroller.
Q4. Which sensor type is better for industrial automation?
Digital sensors are preferred for industrial automation because they provide reliable, interference-free data and flexible communication protocols like RS485 or Modbus.
Q5. Are there sensors with both analog and digital outputs?
Yes. Many advanced distância do laser sensor modules include dual outputs (4–20 mA + RS485 or UART), combining analog feedback with digital communication.
Both analog and digital distance sensors play vital roles in measurement and automation systems.
If your application needs smooth real-time feedback, go for an analog output.
If you need high accuracy and communication stability, choose a digital distance sensor.
Modern laser Sensor ToF modules with dual outputs offer the best of both worlds — making them the ideal choice for industrial automation, robotics, and OEM integration.
https://meskernel.net/laser-distance-measurer-sensor/