Uçuş Süresi (TOF) sensors have quickly become one of the most versatile and widely adopted technologies for non-contact mesafe ölçümü. They appear in drones, robotics, smartphones, industrial automation, 3D cameras, AGVs, warehouse loji̇sti̇k, and consumer electronics. But despite their popularity, many engineers and researchers still have a fundamental question:
How does TOF sensörü work, step by step, and why is it so accurate compared to other ranging technologies?
This comprehensive guide explains the TOF working principle clearly and precisely. We break down how TOF sensörleri emit light, detect reflections, calculate travel time, and convert that information into millimeter-level distance results. Whether you’re integrating a TOF mesafe sensörü into İHA navigation, designing an industrial measurement system, or simply exploring how TOF technology works, this article will give you a deep but easy-to-understand explanation.
1. What Is a TOF Sensor?
A TOF sensor (Time-of-Flight sensor) is an optical distance measurement device that determines how far an object is by calculating the time it takes for emitted light to travel to the target and back. Unlike ultrasonic or kızılötesi sensörler, TOF sensors use light propagation time, which is incredibly fast and requires precise timing electronics.
In simpler terms:
A TOF sensor measures distance by timing how long a photon’s “round trip” takes.
Most TOF sensors use near-infrared laser diodes or VCSEL emitters, combined with high-speed photodiodes or SPAD arrays (Single-Photon Avalanche Diodes).
2. How Does TOF Sensor Work?
The Step-by-Step TOF Working Principle
To fully understand how does TOF sensor works, let’s break the process into four fundamental stages.
2.1 Step 1 — Light Emission
The TOF sensor begins by sending out a burst (or continuous wave) of modulated infrared light from its emitter. Depending on the TOF type, this may be:
- A short laser pulse (Direct TOF)
- A modulated continuous-wave signal (Indirect TOF)
- A coded light pattern for 3D TOF cameras
The key idea:
The clock starts running the moment the light leaves the sensor.
2.2 Step 2 — Light Reflection
The emitted photons hit the target surface (a wall, object, floor, person, etc.) and reflect back toward the sensor. Some materials reflect strongly (white surfaces), others reflect poorly (black matte surfaces), but TOF sensors are designed to detect even very weak returns through amplification and dijital filtering.
2.3 Step 3 — Time Measurement
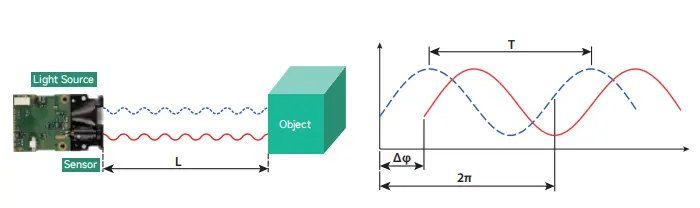
This is the heart of how a TOF sensor works.
The sensor measures the time it takes for the light to return: Distance = (c × t) / 2
Where:
- c = speed of light (~ 3×10⁸ m/s)
- t = measured round-trip time
- /2 because light travels to the target and back
Direct TOF sensors can measure nanosecond- or even picosecond-level timing differences to calculate distance.
Indirect TOF sensors calculate phase shift between transmitted and received signals to determine the travel time.
2.4 Step 4 — Distance Output
Finally, the sensor converts the time (or phase shift) into a readable distance measurement and outputs it via:
- UART / TTL
- RS485 / RS232
- I²C / SPI
- CAN
- Analog 0–10 V or 4–20 mA (through converters)
This is how a TOF sensor produces real-time ranging data for AGVs, robotics, drone altimeters, and industrial measurement systems.
3. Different Types of TOF Sensors and How Each One Works
Although all TOF sensors rely on the same fundamental principle, their internal working mechanisms differ. Understanding these differences helps engineers select the right module for specific applications.
3.1 Direct TOF (dTOF): Pulse-Based Time Measurement
How it works:
- The sensor emits extremely short laser pulses
- The return time is directly measured
- A timer with nanosecond precision calculates the travel time
Avantajlar:
- High accuracy (often ±1 mm to ±10 mm)
- Long range (can reach 20–200 m for industrial modules)
- Excellent for outdoor environments
Use cases:
UAV altimeters, ölçme, long-range distance measurement, outdoor sensing.
3.2 Indirect TOF (iTOF): Continuous-Wave Phase Shift
How it works:
- The sensor emits a modulated continuous wave
- The reflected signal arrives with a phase shift
- Phase difference → distance calculation
Avantajlar:
- Excellent for 2D/3D sensing
- High frame rates
- Widely used in 3D cameras, smartphones, gesture recognition
Use cases:
Face unlock, robotics perception, people tespit, industrial safety curtains.
3.3 3D TOF Cameras (Depth Mapping)
Instead of using a single photodiode, 3D TOF cameras use an array of SPAD pixels that measure the time of flight for each pixel independently.
This produces real-time depth maps used in:
- Automated vehicles
- Obstacle detection and SLAM
- AR/VR
- Industrial machine vision
4. Why TOF Sensors Work Better Than Other Ranging Technologies
To appreciate how TOF sensors work, it helps to compare them with alternative distance-measurement technologies.
4.1 TOF vs Ultrasonic Sensors
| Özellik | TOF Sensor | Ultrasonic |
|---|
| Hız | Speed of light | Slow sound waves |
| Doğruluk | High (mm-level) | Düşük |
| Menzil | Long | Limited |
| Sensitivity | Unaffected by air | Affected by humidity/temp |
| Reflectivity issues | Düşük | Orta |
4.2 TOF vs Infrared Proximity Sensors
Infrared sensors measure intensity, not time.
Intensity-based measurements ≠ accurate time-based measurement.
Thus, TOF sensors outperform IR proximity sensors in precision and reliability.
4.3 TOF vs LiDAR (LIDAR vs TOF)
TOF is a type of LiDAR, but typically refers to short-range, compact modules.
LiDAR (rotating or scanning) is generally:
- Longer range
- More expensive
- Used for mapping or SLAM
TOF modules are:
- More compact
- Lower power
- Ideal for embedded systems (UAVs, AGVs, robots)
5. TOF Sensor Accuracy: What Factors Influence Performance?
Understanding how TOF sensor works also requires understanding what affects accuracy.
Key influencing factors:
- Surface reflectivity
- Ambient infrared noise
- Temperature drift
- Lens contamination
- Multi-path reflections
- Target orientation
- Measurement frequency (sample rate)
Industrial TOF modules include compensation algorithms such as:
- Ambient light filtering
- Temperature calibration
- Adaptive thresholding
- Multi-sample averaging
- Optical filtering
These improve stability and accuracy in harsh environments.
6. Real-World Applications: Where Does TOF Working Principle Matter Most?
TOF technology is used everywhere due to its simple working principle and reliable performance.
Common TOF applications include:
- Drones & UAVs: altitude hold, terrain following
- AGVs & AMRs: anti-collision, navigation
- Robotik: SLAM, object avoidance, arm positioning
- Endüstriyel otomasyon: presence detection, distance control
- Smartphones: face recognition, AR depth sensing
- Lojistik: pallet detection, cargo measurement
- Retail automation: people counting, space analysis
- Smart cities: traffic monitoring, parking systems
In each of these cases, engineers benefit greatly from understanding how a TOF sensor works when selecting the right module and optimizing performance.





7. How to Select the Right TOF Sensor (Engineer Checklist)
Once you understand how TOF sensors work, choosing a module becomes much easier.
Here’s what to evaluate:
✔ Measurement range
(Short-range consumer TOF vs long-range industrial TOF)
✔ Accuracy requirements
(e.g., ±1 mm for indoor robotics, ±5–10 cm for outdoor ranging)
✔ Update frequency
(High-speed robotics requires 100–1000 Hz)
✔ Ambient light performance
(Choose NIR filters for outdoor applications)
✔ Interface compatibility
(UART, RS485, CAN, I²C, Analog 0–10 V)
✔ Power consumption
(Battery-operated drones need low-power TOF modules)
A Simple Summary of How does TOF Sensor Works
To recap:
- A TOF sensor emits infrared light
- The light reflects off the target
- The sensor measures the return time
- Time × speed of light → distance
- Algorithms enhance accuracy and stability
Once you clearly understand how does TOF sensor works, you can select the right module, optimize your system, and build highly reliable ranging solutions for drones, robots, industrial equipment, and more.
-
How Does TOF Sensor Work?
A TOF (Time-of-Flight) sensor works by emitting a beam of infrared light, detecting the reflected signal, and measuring how long the light takes to return. The sensor calculates distance using the speed of light and the measured round-trip travel time.
-
How does TOF Sensor Works — Step-by-Step
Light Emission – The sensor sends out a laser pulse or modulated infrared beam.
Yansıma – The light hits the target and bounces back to the sensor’s receiver.
Zaman Ölçümü – The sensor measures the time delay (or phase shift) between emission and return.
Mesafe Hesaplama – Distance is computed using the formula:
Distance = (c × t) / 2
where c is the speed of light.
Çıktı – The sensor converts the result into a distance reading (mm/cm/m) via UART, I²C, RS485, or analog output.
In Simple Terms
A TOF sensor measures distance by timing a photon’s round trip to the target and back.
-
What is the principle of a TOF sensor?
A TOF sensor measures distance by calculating how long emitted infrared light takes to travel to a target and back. It uses the speed of light and either pulse timing or phase-shift detection to compute distance accurately.
-
Why is TOF accurate for distance measurement?
Because TOF relies on the speed of light instead of signal intensity, it provides stable millimeter-level accuracy regardless of color, texture, or ambient light. Algorithms further improve precision through filtering and temperature compensation.
-
What is the difference between Direct TOF and Indirect TOF?
Direct TOF measures the actual return time of a laser pulse. Indirect TOF measures the phase shift between continuous-wave signals. Direct TOF gives long-range accuracy, while Indirect TOF supports high-speed 3D depth sensing.
https://meskernel.net/laser-based-distance-sensors/